Eggplant Growing Stages
Published: 29 Jan 2025
Eggplant, also known as brinjal, is a seasonal and rewarding vegetable from the nightshade family. In this blog post, we will explore the seven different eggplant growing stages. This stunningly beautiful and delightfully tasty veggie grows annually in your garden, offering a unique cultivation journey that is as fascinating as it is rewarding.

What is Eggplant
Eggplant is a type of fruit commonly used in cooking. It is a large, oval-shaped vegetable with purple or green skin and white flesh. Eggplants are native to Asia and are now grown in many parts of the world. They are often used in ratatouille, moussaka, and baba ghanoush dishes. Basil is a good companion plant for eggplant. Traditional medicine also uses eggplants to treat various ailments, including digestive issues and skin conditions.
What is eggplant Color?
Eggplant is a type of fruit that is typically purple, although it can also be white or yellow. The purple color of eggplant is caused by anthocyanin pigments, which have been linked to various potential health benefits.
Some varieties of eggplant, such as the white or yellow types, do not contain as much anthocyanin and may have slightly different nutritional profiles. like all fruits and vegetables, the color of eggplant can vary depending on ripeness.
7 Eggplant Growing Stages
Planting
The first stage of the brinjal plant growing stage is called planting. The planting stage is a crucial phase in the brinjal plant growth stages. It involves soil preparation rich in organic matter, well-draining, and planting the seeds at the correct depth and distance.
The seeds should be sown at a depth of about 1/4 inch, and seedlings should be spaced about 18 to 24 inches apart to allow for healthy growth. Adequate sunlight, regular watering, and balanced fertilization are also crucial during this stage.
The planting stage sets the foundation for the subsequent stages in the eggplant growing process, including germination, flowering, and fruiting.
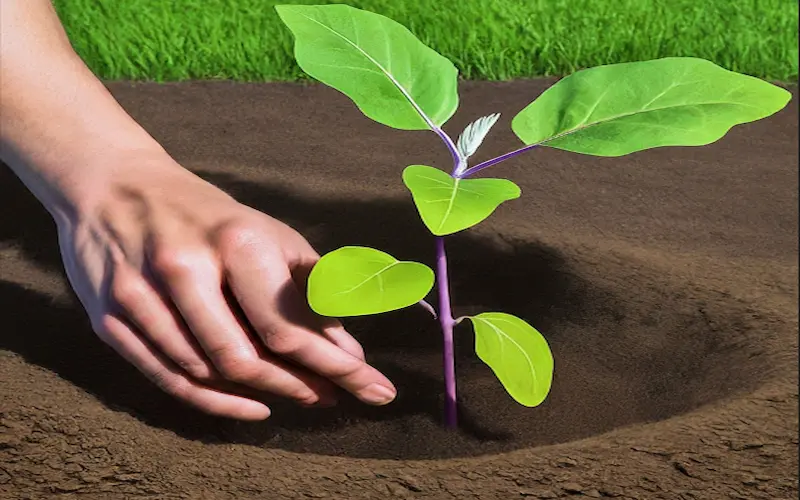

The ideal time for planting eggplant seeds is about 6 to 9 weeks before the last spring frost date. They need a long, warm season to produce fruit.
When it comes to planting the seeds, embed them about a quarter inch deep into the soil. Space them at least 4 to 6 inches apart to allow ample room for growth.
Selecting Varieties
The next step is selecting the right seeds. Opt for a variety known to perform well in your region’s climate. You can purchase seeds from a reputable online seed store or your local nursery. Selecting the appropriate varieties is a critical aspect of the eggplant growing stages.
The choice of variety directly impacts the plant’s growth, yield, and disease resistance. Some popular varieties include Black Beauty, Long Purple, and Japanese White Egg, each having distinct growth requirements and characteristics.
Understanding the specific needs of these varieties can significantly enhance the success of your eggplant growing stages. When choosing a suitable variety, it’s crucial to consider factors such as climate, soil type, and available space. Rotating eggplant varieties yearly is advisable to prevent disease build-up and promote a healthy, productive garden.
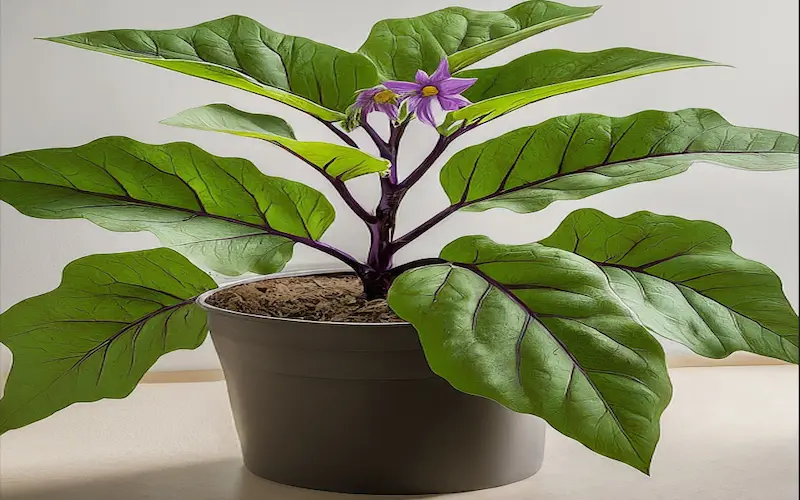

Seed Germination Stage of Brinjal Plant Growing Stages
After 7 to 10 days, the Seed starts to sprout, breaking through the soil’s surface. It is called germination, which means the first signs of life a tiny green sprout. However, if it’s been over two weeks and you still see no signs of germination, the seeds are likely either not viable or the conditions are not optimal.
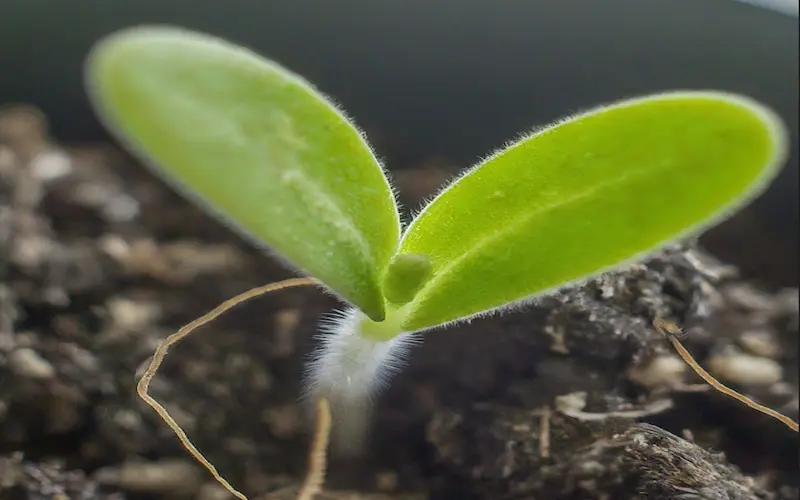

Seedling Development
Nutrition is another critical aspect of seedling care. Fertilize the seedlings with a balanced liquid fertilizer every two weeks. This will provide them with the necessary nutrients to grow strong and healthy.
As your seedlings grow, they might become susceptible to pests and diseases. Keep a close eye on them and immediately act at the first sign of trouble. You can use organic pesticides or introduce beneficial insects to your garden to keep pests in check.
As they grow bigger, your seedlings may need more space. This is when you should transplant them into larger containers or directly into your garden, taking care not to damage the roots.

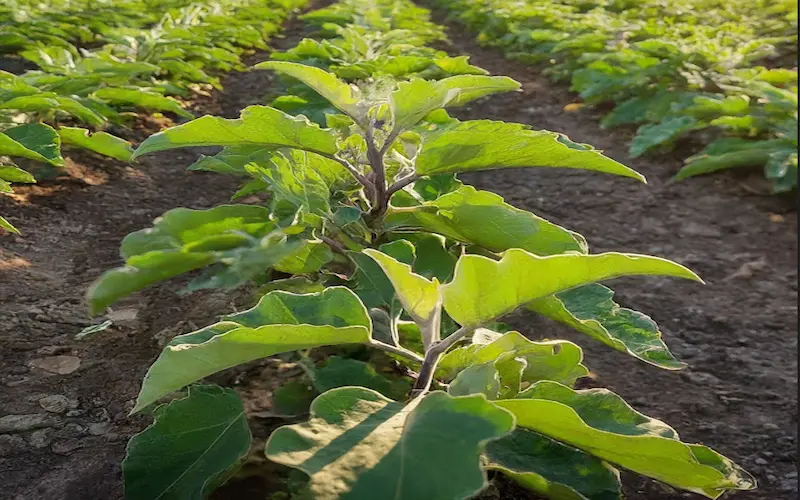
Vegetative Growth
At this point, the seedlings grow larger and sprout oval-shaped leaves with wavy edges and a slightly fuzzy texture. This stage takes place around 7-14 days after the cotyledon stage. Amidst this rapid growth, it’s crucial to watch out for pests and diseases.
Consider companion planting, a method of growing different plants together for mutual benefit to encourage healthier growth. Also, remember that the plants will require 1-2 inches of water per week during this phase.

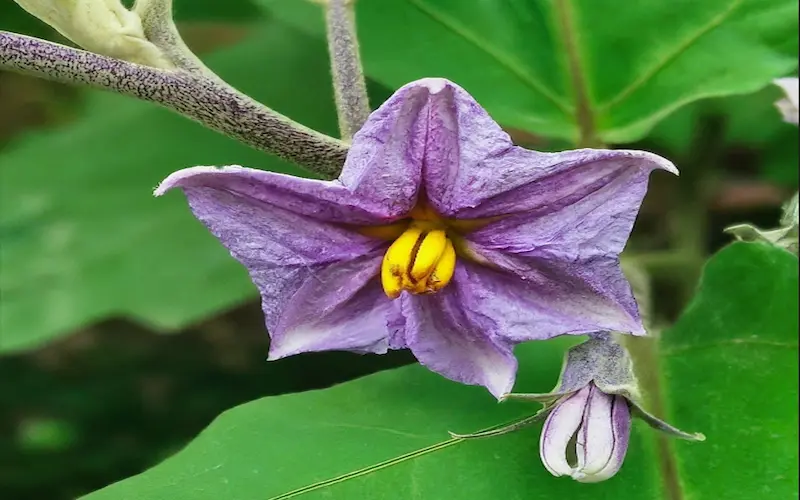
Flowering of Eggplant Growing stages
This stage starts approximately 60 days after you’ve sown the seeds. At this time, your eggplant plants will begin to produce pale purple, star-shaped flowers. These flowers are not just a delightful sight; they attract pollinators like bees and butterflies, essential for the subsequent fruiting stage. Watch for the emergence of distinct flowers, a sign of the transition to the next stage.

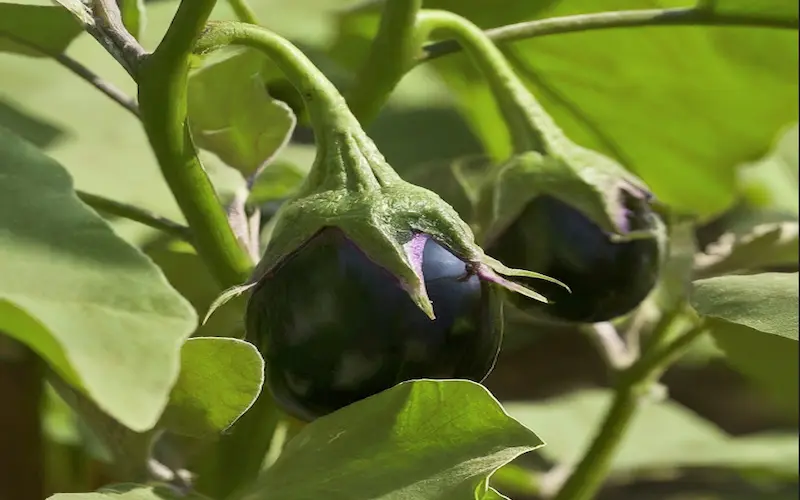
Fruiting
This stage usually takes about 7 to 14 days. As the flowers fall off, tiny fruits emerge in mature brinjal color, generally a deep purple or black. This is known as the fruiting of eggplant growing stages. However, the time from Seed to harvest can vary depending on the variety, ranging from 75 to 140 days.
Harvesting
Harvest ripe eggplants carefully to enjoy the fruits of a successful cultivation journey. Eggplants are ready for harvest when firm and have a glossy skin. Size is only sometimes an indicator of maturity, as some varieties stay small even when fully ripe.

Harvest your eggplants by cutting the stem above the fruit with a sharp knife or pruner. Be careful not to damage the plant or the fruit. Wear gloves if the plant has spiky thorns.
The Life Cycle of Eggplant
The life cycle of an eggplant starts with tiny seeds planted in the soil. These seeds germinate into seedlings, and when they’re strong enough, they are carefully transplanted into a garden or a suitable container. As these young plants grow, they enter the vegetative stage, developing a robust leaf and stem framework.
As the eggplant continues to mature, it transitions to the flowering stage, producing distinct flowers. These flowers play a crucial role in the next phase, where they transform into small green structures in the early stage of eggplants. Over time, these structures mature into the familiar deep-purple or glossy white eggplants we commonly see.
The final stage is harvesting, where the mature eggplants are carefully picked, completing the cycle and providing a bounty of delicious fruits. Understanding and managing each stage is essential for successful and rewarding brinjal plant cultivation.

Conclusion
In my opinion, eggplant’s growth from seed to harvest is an incredible journey that requires understanding and appreciating its different growth stages. Starting with the proper seed selection, we’ve seen how eggplants evolve from germination and seedling development to vegetative growth and care.
The growth process doesn’t end here; it continues through the flowering and fruiting stages until it’s time for harvest.
Depending on the variety and growing conditions, eggplants typically take about 70 to 85 days to grow from seeds to mature, harvest-ready fruits.
The best season to grow eggplant is typically during the warm months of spring and summer, when temperatures range between 75°F and 90°F (24°C and 32°C). These conditions provide the ideal environment for eggplant plants’ successful germination, growth, and fruiting.
One eggplant plant can typically produce several fruits, with the exact number depending on factors like the plant’s health, care, and growing conditions. On average, a healthy eggplant plant may yield anywhere from four to six fruits during a growing season.
The best fertilizer for eggplants is a balanced, all-purpose fertilizer with equal amounts of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. This helps promote healthy plant growth and robust foliage and encourages the development of plentiful, flavorful eggplants.
There are 17 types of eggplant in the market. They are called Thai eggplant, globe eggplant, Japanese eggplant, Orient charm eggplant, purple shine, black beauty, heirloom eggplant, Nadia, Rosa Bianca, white eggplant, graffiti eggplant, etc.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks



- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks