From Seed to Harvest: Unleashing the Potential of Gram Crop Farming for Profitable Returns
Published: 26 Oct 2025
Gram, also known as chickpea, is one of the most popular pulse crops grown in many parts of Asia and Africa. It belongs to the legume family and is known for its high protein content. Farmers grow gram for both household use and commercial purposes. The plant has small pods containing one or two seeds, which are either brown (Desi type) or light-colored (Kabuli type).
What is Gram Crop (Chickpea)?
Gram is a cool-season crop that grows well in dry, mild climates. It is mainly cultivated in countries like India, Pakistan, and Australia. The crop does not need too much water, which makes it suitable for semi-arid regions. Its deep root system helps it survive in less fertile soils. People use chickpeas in many food dishes, and they are also processed into flour for snacks and sweets.
Why Gram Is an Important Pulse Crop in Agriculture
Gram plays an important role in agriculture because it is a major source of plant-based protein. It is often called the “poor man’s meat” due to its high nutritional value and affordability. Besides being a healthy food, it helps farmers earn a good income, especially during the rabi season. The straw left after harvesting is also used as animal feed, which adds more value to the crop.
Role of Gram in Soil Health and Sustainable Farming
Gram is not only good for people but also for the soil. Like other legumes, it can fix nitrogen from the air and store it in the soil through special root nodules. This natural process reduces the need for chemical fertilizers and improves soil fertility for the next crop. Farmers often grow gram in rotation with cereals like wheat to maintain soil balance and increase overall farm productivity.
In short, grain crop farming supports sustainable agriculture by saving water, improving soil health, and providing nutritious food for people and livestock alike. Confused by talk of local solar, batteries, and grid rules? Many people ask, “What is distributed power generation?” This guide will help you calm the noise and provide a clear plan. We explain the idea in plain words and show how it works step by step. We cover the key parts, the link with the grid, and real uses for homes and businesses. We also outline costs, savings, safety, and simple steps to plan and compare quotes. You will finish ready to make a confident, informed choice.

Advantages of gram crop farming
| Advantages of gram crop farming |
|---|
Gram crop farming offers numerous advantages and benefits, making it an attractive option for farmers
|
Understanding the growth cycle of gram crops
To unleash the potential of gram crop farming, it is crucial to understand the growth cycle of these crops. Gram crops undergo a typical life cycle consisting of four main stages: germination, vegetative growth, flowering, and pod development. Each stage requires specific conditions and care to ensure optimal growth and yield.
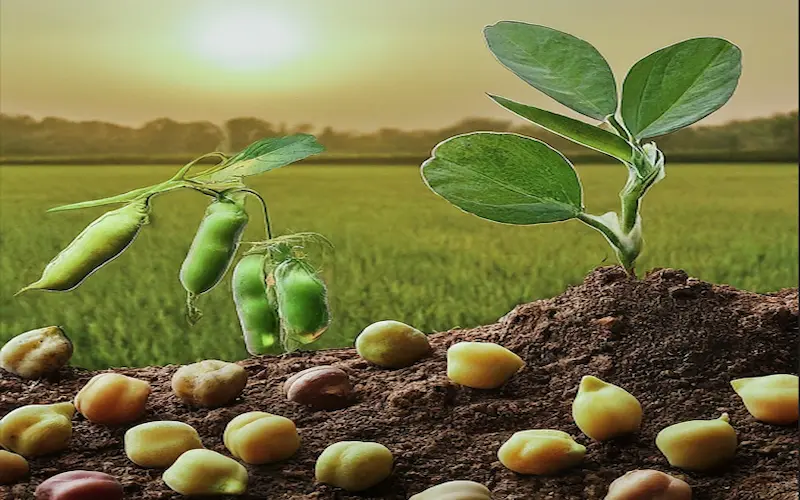

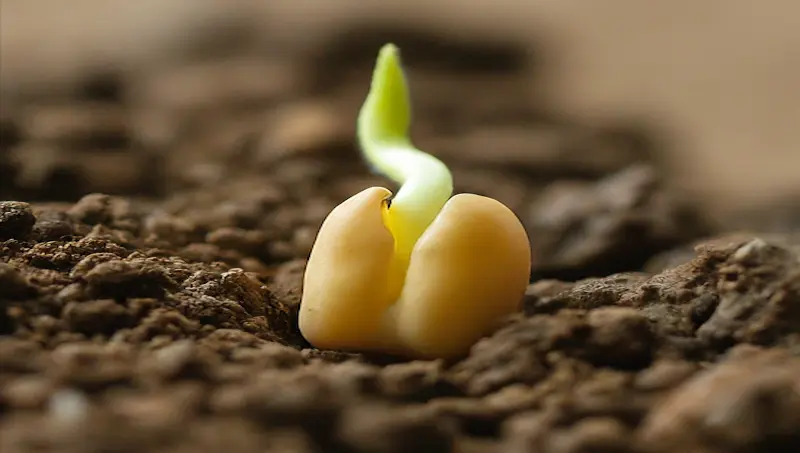
Germination stage
The germination stage begins when the seed absorbs water and swells, eventually leading to the emergence of the radicle. During this stage, it is vital to provide adequate moisture and warmth to facilitate proper germination. Once germination occurs, the crop enters the next stage.

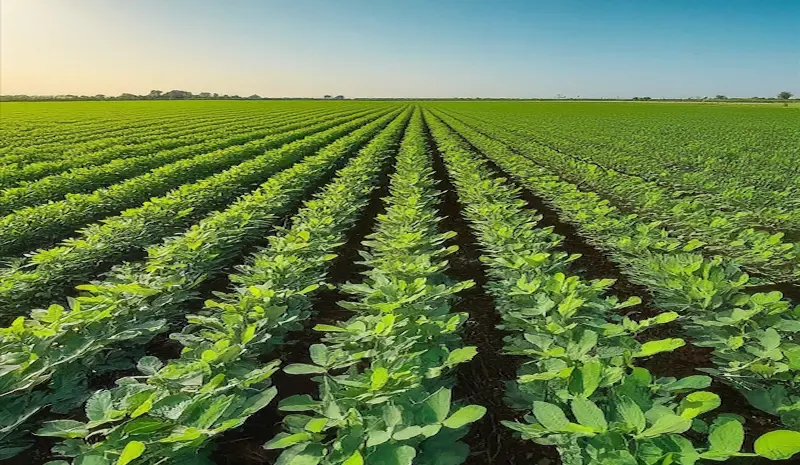
Vegetative growth stage.
The development of leaves and branches characterizes the vegetative growth stage. Providing sufficient nutrients and water is crucial to support healthy plant growth at this stage.

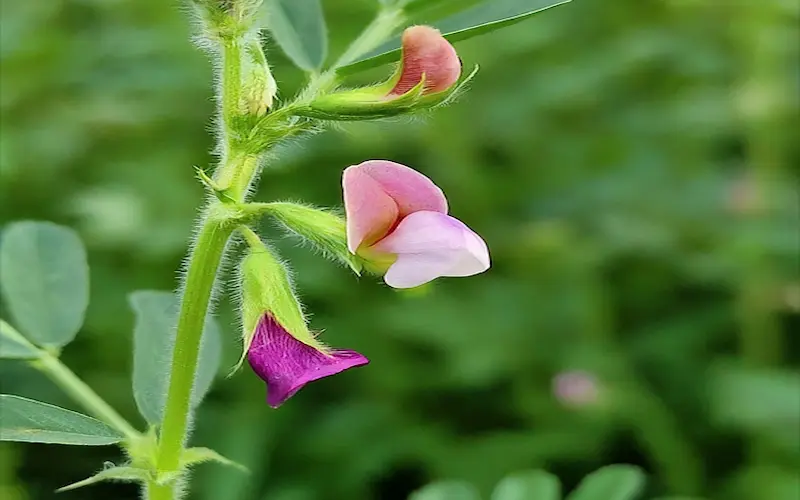
The flowering stage
The flowering stage marks a critical period in the growth cycle of gram crops as it determines the potential yield. During this stage, bees and other pollinators play a crucial role in facilitating pollination, leading to pod formation. Ensuring the presence of pollinators and maintaining favourable environmental conditions are essential for successful flowering.

Pod development stage
The pod development stage starts when the gram crop matures and the pods fill with seeds. Regular monitoring of the crop’s health and timely irrigation are essential during this stage to prevent stress and ensure the development of plump and healthy pods.
Soil preparation and seed selection for gram crop farming
Proper soil preparation and seed selection are fundamental to successful gram crop farming. Before planting, it is crucial to ensure that the soil is well-drained, rich in organic matter, and has a pH level between 6.0 and 7.5. A soil test can provide valuable insights into the soil’s nutrient composition, allowing farmers to make informed decisions regarding fertilization.
Choosing high-quality seeds is imperative for achieving desirable yields when it comes to selection. The selected seeds should be free from diseases, pests, and genetic abnormalities. Additionally, selecting seeds that exhibit desirable traits such as early maturity, disease resistance, and high yield potential can significantly impact the profitability of gram crop farming.

Planting and caring for gram crops
Proper planting and care techniques are essential to ensure gram crops’ healthy growth and development. The ideal time for planting gram crops varies depending on the region and climate. Generally, 10- 15°C is the perfect soil temperature for sowing the seeds.
Planting depth and spacing are critical factors to consider.
The seeds should be sown at approximately 2-3 centimeters with a spacing of 10-15 centimeters between plants. This spacing allows room for the plants to grow and receive adequate sunlight and airflow.
Regular irrigation is necessary to maintain soil moisture and prevent drought stress.
However, excessive humidity should be avoided to prevent waterlogging and the development of diseases. Applying a balanced fertilizer at specific growth stages can enhance plant growth and yield.

Common pests and diseases in gram crop farming and their management
Like any other agricultural practice, gram crop farming is susceptible to various pests and diseases that adversely affect yield and profitability. Some common pests that affect gram crops include aphids, pod borers, and gram pod flies. These pests can cause significant damage to the plants, leading to reduced yield.
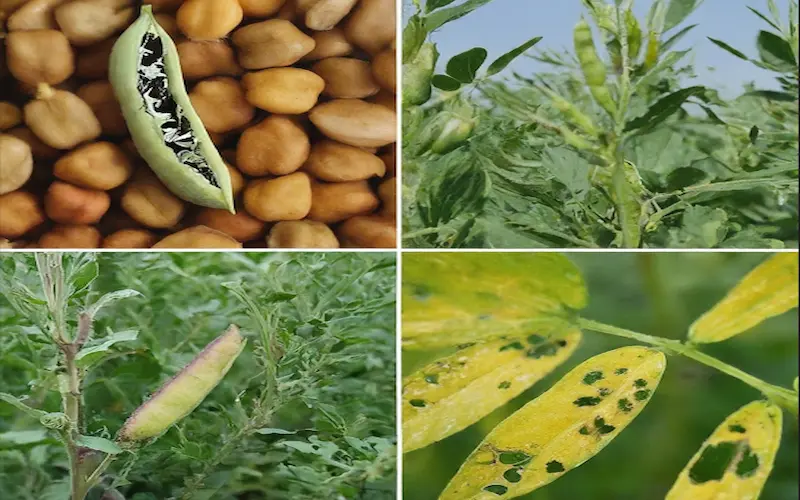

Farmers can employ integrated pest management strategies to manage these pests, which involve a combination of cultural, mechanical, and chemical control methods. Cultural practices such as crop rotation, intercropping, and proper plant spacing can help reduce pest populations. Mechanical control methods include physically removing pests from the plants, while chemical control involves the judicious use of pesticides.
In addition to pests, gram crops are vulnerable to diseases such as fusarium wilt, ascochyta blight, and root rot. Preventive measures such as crop rotation, seed treatment, and proper drainage can help minimize the risk of disease outbreaks. Farmers may need to use fungicides or other disease management strategies in severe cases.

Harvesting and post-harvest practices for gram crops
Harvesting is also a vital stage in gram crop farming, as it determines the quality and market value of the produce. Gram crops are typically harvested when the pods turn brown and dry, indicating maturity. Timing is crucial, as gathering too early can result in underdeveloped seeds, while delaying the harvest can lead to shattering and seed loss.
Manual or mechanical methods can be employed to harvest gram crops, depending on the scale of cultivation. Manual harvesting involves cutting plants near the ground using sickles or knives. On the other hand, mechanical harvesters are suitable for larger-scale operations, enabling efficient harvesting and minimizing labor requirements.
Once harvested, proper post-harvest practices are essential to maintain the quality and marketability of the gram crops. Threshing, cleaning, and drying the harvested pods are crucial to removing impurities and reducing moisture content. Proper storage conditions, including temperature and humidity control, are necessary to prevent insect infestation and mold growth. Adequate packaging and labeling also contribute to the marketability of the gram crops.

Marketing and selling gram crops for profitable returns
Effective marketing and selling strategies are essential to achieving profitable returns from gram crop farming. Building relationships with potential buyers, such as local markets, grocery stores, restaurants, and food processors, can create a steady demand for the produce. Participating in farmers’ markets, agricultural fairs, and trade shows can also help raise awareness and generate sales.
Utilizing digital platforms and social media can significantly expand the reach of the gram crop produce. Creating a website or an online store allows farmers to showcase their products and receive customer orders. Engaging in online marketing campaigns, such as email newsletters and social media advertisements, can also help attract new customers.
Moreover, diversifying the product range by offering value-added products, such as gram flour, roasted, and canned, can increase profitability. These products cater to different consumer preferences and have a longer shelf life, allowing farmers to tap into new markets and achieve higher profit margins.
Case studies of successful gram crop farmers
To further illustrate the potential of gram crop farming for profitability, let’s explore a few case studies of successful farmers in this sector. These farmers have implemented innovative techniques and strategies to maximize their yields and market value.
Case Study 1: Mr. Patel, a gram crop farmer from Gujarat, India, has adopted organic farming practices, which have increased the market demand for his produce. By focusing on sustainable cultivation methods and emphasizing the nutritional benefits of his gram crops, Mr Patel has successfully established a loyal customer base and achieved higher prices for his products.
Case Study 2: Mrs. Smith, a gram crop farmer from California, USA, has leveraged technology to expand her market reach. She has developed an online store and regularly engages with customers through social media. By offering a wide range of gram crop products, including gluten-free options, Mrs Smith has attracted health-conscious consumers and established a profitable business.
Conclusion and final thoughts on the potential of gram crop farming for profitability
Gram crop farming presents a promising opportunity for farmers to achieve profitable returns. With its adaptability, high nutritional value, and long shelf life, gram crops have the potential to meet the growing demand for nutritious and sustainable food sources.
By understanding the growth cycle, implementing proper cultivation practices, and adopting effective marketing strategies, farmers can unleash the full potential of gram crop farming. As demonstrated by the case studies, innovation and creativity can further enhance profitability in this sector. If you want to venture into agriculture or diversify your existing farm, consider gram crop farming a lucrative option.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks



- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks