Top 10 Summer Vegetables in Pakistan: Easy to Grow & Harvest
Published: 24 Mar 2025
It gets very hot in Pakistan in the summer, but it’s also the best time to grow many kinds of veggies. Tomatoes, okra, and cucumbers do well in temperatures above 30°C. They can be grown in home gardens, patios, or pots if they get enough care. When growing fresh, organic veggies this summer, you must pick the right plants and use the proper methods.
Importance of Choosing the Right Vegetables for Hot Weather
Not all vegetables can survive Pakistan’s scorching summers. Some require cooler temperatures and may struggle in extreme heat. Choosing heat-resistant crops ensures successful growth and reduces plant stress. Vegetables like tomatoes, cucumbers, and pumpkins adapt well to the hot climate, needing less maintenance and fewer resources to thrive. Selecting the right vegetables also means less water wastage and higher productivity in home gardens.
Benefits of Growing Summer Vegetables at Home
- Fresh & Organic Produce: Homegrown vegetables are free from chemicals and pesticides.
- Cost-Effective: Saves money on store-bought vegetables.
- Sustainable & Eco-Friendly: Reduces dependency on markets and supports self-sufficiency.
- Healthier Lifestyle: Eating freshly harvested vegetables improves nutrition and overall well-being.
- Great for Small Spaces: Many summer vegetables grow well in pots, ideal for balconies and small gardens.
Growing summer vegetables in Pakistan is easy and rewarding when done right. Let’s explore the best summer vegetables and how to grow them successfully.
Summer Vegetable List in Pakistan
In the summer season, a variety of vegetables are grown in Pakistan. Some of them are listed below
1. Tomato
2. Cucumbers
3. Okra (Ladyfinger)
4. Bitter Gourd (Karela)
5. Eggplant (Brinjal)
6. Green Beans
7. Bottle Gourd (Lauki)
8. Squash
9. Corn
10. Spinach
Vegetables Growing Season Chart in Pakistan
| Vegetable | Sowing Time | Germination Time | Harvest Time | Best Growing Conditions |
| Tomato (ٹماٹر) | Feb – April | 7-14 days | 60-80 days | Full sun, well-drained soil |
| Okra (بھنڈی) | March – June | 5-12 days | 50-60 days | Full sun, regular watering |
| Bitter Gourd (کریلا) | March – July | 7-14 days | 60-70 days | Needs support, moderate watering |
| Cucumber (کھیرا) | March – July | 3-10 days | 45-60 days | Needs trellis, moist soil |
| Eggplant (بینگن) | Feb – May | 7-14 days | 80-100 days | Full sun, fertile soil |
| Pumpkin (کدو) | March – June | 7-14 days | 90-120 days | Needs space, full sun |
| Squash (لوکی, گھیا توری) | March – July | 7-10 days | 50-70 days | Needs support, moderate watering |
| Chili Pepper (مرچ) | Feb – June | 7-14 days | 60-80 days | Full sun, moderate watering |
| Spinach (پالک) | March – May | 5-10 days | 40-50 days | Partial shade, moist soil |
| Watermelon (تربوز) | Feb – May | 5-12 days | 80-100 days | Full sun, sandy soil |
Summer Season Vegetables in Pakistan
Pakistan’s hot and dry summer creates ideal conditions for many vegetables that thrive in full sunlight and high temperatures. Gardeners can enjoy a bountiful harvest even in extreme weather by choosing heat-resistant, drought-tolerant crops. Whether you have a large backyard or a small balcony, growing summer vegetables at home is easy with the proper selection and care.
Summer Vegetables Growing Time
Summer vegetables thrive in warm temperatures and require plenty of sunlight. The best time to plant them is in early spring after the last frost, as they need consistent warmth to grow. Common summer vegetables like tomatoes, cucumbers, peppers, and eggplants grow well between April and July, depending on the region.
These crops require well-drained soil, regular watering, and protection from extreme heat. Fast-growing options like zucchini and green beans can be harvested within 6–8 weeks, while longer-season vegetables like melons may take up to 90 days to mature.
Summer Vegetables Growing Time in Pakistan
In Pakistan, summer vegetables are planted from February to April in warmer regions and March to May in cooler areas. The country’s hot climate supports the growth of vegetables like okra, pumpkin, bitter gourd, ridge gourd, and chillies.
These crops thrive in temperatures between 25°C to 35°C and require consistent moisture. Harvesting usually starts from May to September, depending on the vegetable type. In extreme heat, mulching and shade nets help protect plants from sun damage, ensuring a healthy yield.
Summer Vegetables Growing Time Chart
| Vegetable | Growing Time (General) | Growing Time in Pakistan | Harvest Time |
| Tomato | April – July | February – April | 60 – 80 days |
| Cucumber | April – August | March-May | 50 – 70 days |
| Eggplant | April – July | February – April | 70 – 90 days |
| Okra (Ladyfinger) | March-August | February – May | 50 – 60 days |
| Pumpkin | April – August | March-August | 90 – 120 days |
| Bitter Gourd | March-August | February – April | 50 – 60 days |
| Ridge Gourd | March – August | February – April | 50 – 60 days |
| Chili Pepper | April – July | February – April | 70 – 100 days |
| Green Beans | April – August | March-May | 50 – 60 days |
| Watermelon | March – July | February – April | 80 – 100 days |
| Muskmelon | March – July | February – April | 70 – 90 days |
Summer Growing Conditions in Pakistan
Pakistan’s summer season lasts from March to September, with peak temperatures reaching 40°C or higher in many regions. Some key factors to consider when growing vegetables during summer include:
✅ Soil Preparation: Use well-draining, nutrient-rich soil to prevent root rot and promote healthy growth. Adding organic compost improves fertility.
✅ Watering Requirements: Deep watering in the early morning or late evening helps plants survive the scorching heat. Avoid overwatering, as it can cause fungal diseases.
✅ Sunlight Needs: Most summer vegetables require 6-8 hours of direct sunlight daily for proper growth and fruit production.
✅ Pest Control: High temperatures attract pests like aphids, whiteflies, and caterpillars. Use neem oil, organic pesticides, or companion planting to keep them away.
Let’s explore the top 10 summer vegetables that grow best in Pakistan!
Top 10 Summer Vegetables in Pakistan in Urdu
Here are the names of the 10 best vegetables in Pakistan in Urdu:
Tomato – ٹماٹر
Okra (Lady Finger) – بھنڈی
Cucumber – کھیرا
Eggplant (Brinjal) – بینگن
Bottle Gourd – لوکی
Bitter Gourd – کریلا
Spinach – پالک
Lady Finger – بھنڈی
Pumpkin – کدو
Capsicum (Bell Peppers) – شملہ مرچ
Tomatoes
Here’s a simple guide on how to grow tomatoes at home:
Tomatoes grow well in Pakistan’s hot climate. They need well-drained soil and full sun to thrive. Plant them from February to April for the best results. Water them regularly to improve growth. Fresh tomatoes are used for salads, curries, and sauces. They are rich in vitamin C and antioxidants. Harvesting starts within 60-80 days after planting. Tomatoes can be grown in pots, containers, or open fields. Protect them from pests like aphids and whiteflies using natural insect repellents or neem oil for better yield.
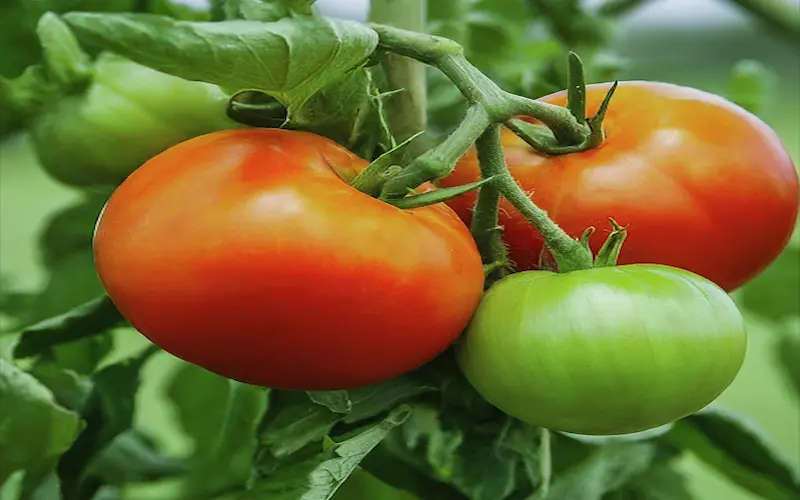

Cucumbers
- Choose the Right Variety: Select a variety suited for your climate, such as Armenian or Lemon cucumbers, which are heat-tolerant.
- Start from Seeds: Sow cucumber seeds directly into the garden after the last frost when the soil is warm.
- Prepare the Soil: Use well-draining, fertile soil enriched with compost. Cucumbers prefer slightly acidic to neutral soil.
- Planting: Plant seeds 1 inch deep and space them 12-18 inches apart in rows or hills.
- Sunlight: Ensure the plants receive 6-8 hours of direct sunlight daily.
- Watering: Water regularly, keeping the soil consistently moist, but avoid waterlogging.
- Support the Vines: Use trellises or stakes to support climbing cucumber vines, which keeps the fruit off the ground and makes harvesting easier.
- Fertilization: Apply a balanced fertilizer every 2-3 weeks, especially during the growing and fruiting stages.
- Pest Control: Watch for pests like aphids and cucumber beetles, and use organic pesticides or neem oil as needed.
- Harvesting: Harvest cucumbers when they are firm, green, and about 6-8 inches long before they become too large and seedy.
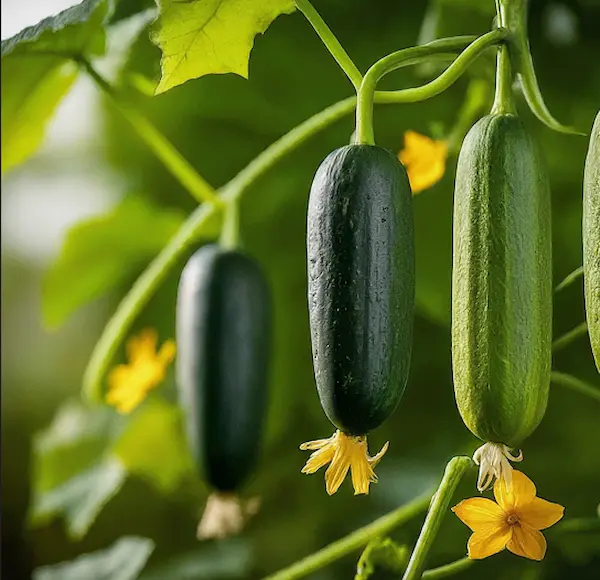

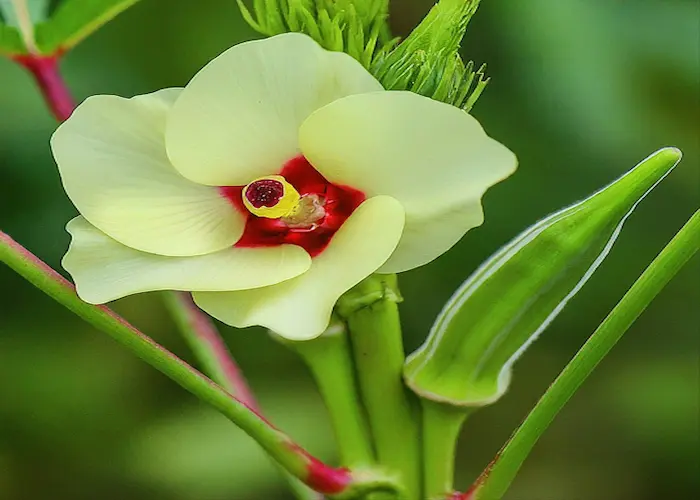
Okra (Ladyfinger)
- Choose the Right Variety: Pick varieties like Clemson Spineless or Emerald that thrive in hot climates.
- Start from Seeds: Soak seeds overnight to speed up germination, then plant them directly in the garden.
- Prepare the Soil: Okra prefers well-drained, sandy loam soil with plenty of organic matter.
- Planting: Sow seeds 1 inch deep and space them 12-18 inches apart in rows.
- Sunlight: Ensure 6-8 hours of direct sunlight for optimal growth.
- Watering: Water regularly, especially during dry spells, but avoid overwatering.
- Fertilization: Apply a balanced fertilizer every 3-4 weeks to encourage healthy growth.
- Pest Control: Look out for pests like aphids and flea beetles, and treat them with organic insecticides if necessary.
- Harvesting: Harvest okra pods when they are 3-5 inches long and tender, usually about 60 days after planting.

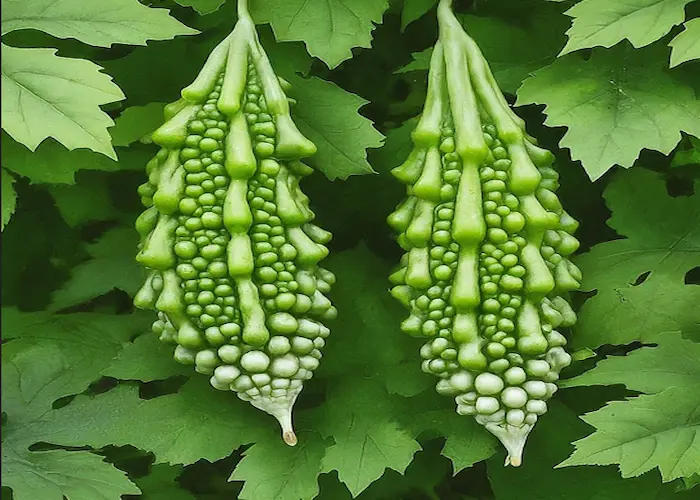
Bitter Gourd (Karela)
- Choose the Right Variety: Select a local variety like Faisalabad Long or Peshawari that is well-suited to the climate.
- Start from Seeds: To speed up germination, soak seeds in water for a few hours before sowing them directly in the garden.
- Prepare the Soil: Use well-drained, rich soil with plenty of organic matter.
- Planting: Plant seeds 1 inch deep and space them 12-18 inches apart.
- Sunlight: Ensure total sun exposure for at least 6-8 hours daily.
- Watering: Water regularly, keeping the soil consistently moist but not soggy.
- Support the Vines: Provide trellises or other supports for the vines to climb.
- Fertilization: Apply a balanced fertilizer every 2-3 weeks during the growing season.
- Pest Control: Monitor for pests like fruit flies and aphids, and use organic remedies if necessary.
- Harvesting: Pick bitter gourds when they are 4-6 inches long and still green before they start turning yellow.

Eggplant (Brinjal)
- Choose the Right Variety: Varieties like Purple Long or Round Brinjal are well-adapted to hot climates.
- Start from Seeds: Start seeds indoors for 6-8 weeks before transplanting them outdoors or directly sowing in the garden.
- Prepare the Soil: Use fertile, well-drained soil enriched with compost or organic matter.
- Planting: Transplant seedlings when they are 4-6 inches tall, spacing them 18-24 inches apart.
- Sunlight: Ensure the plants get 6-8 hours of direct sunlight daily.
- Watering: Keep the soil evenly moist, but avoid waterlogging. Mulch around the plants to retain moisture.
- Fertilization: Fertilize with a balanced fertilizer every 3-4 weeks during the growing season.
- Pest Control: Watch out for pests like aphids and spider mites, and use organic pest control methods as needed.
- Harvesting: Harvest eggplants when shiny, firm, and have reached the desired size, usually 70-85 days after planting.

Green Beans
- Choose the Right Variety: Bush and pole beans do well in hot climates. Choose a variety that suits your space.
- Start from Seeds: Sow seeds directly into the garden after the last frost.
- Prepare the Soil: Use well-drained, fertile soil enriched with organic matter.
- Planting: Plant seeds 1 inch deep, spacing them 2-4 inches apart in rows.
- Sunlight: Ensure 6-8 hours of direct sunlight daily.
- Watering: Keep the soil moist, especially during flowering and pod formation.
- Support the Plants: Provide trellises or stakes for pole beans to climb.
- Fertilization: Use a low-nitrogen fertilizer every 2-3 weeks to promote flowering and pod development.
- Pest Control: Look for pests like aphids and bean beetles and treat them with organic methods.
- Harvesting: Harvest beans when tender and about 4-6 inches long before the seeds inside fully develop.

Bottle Gourd (Lauki)
- Choose the Right Variety: Choose local varieties like Peshawari or Long Bottle Gourd, which are well-suited to the climate.
- Start from Seeds: Soak seeds overnight and plant them directly in the garden.
- Prepare the Soil: Use rich, well-drained soil with plenty of organic matter.
- Planting: Plant seeds 1 inch deep and space them 12-18 inches apart.
- Sunlight: Ensure total sun exposure for at least 6-8 hours daily.
- Watering: Water regularly, keeping the soil moist but not waterlogged.
- Support the Vines: Provide strong supports or trellises for the vines to climb.
- Fertilization: Fertilize with a balanced fertilizer every 2-3 weeks during the growing season.
- Pest Control: Watch for pests like aphids and caterpillars, and use organic pest control methods if needed.
- Harvesting: Harvest bottle gourds when tender and about 12-15 inches long, usually around 60-70 days after planting.
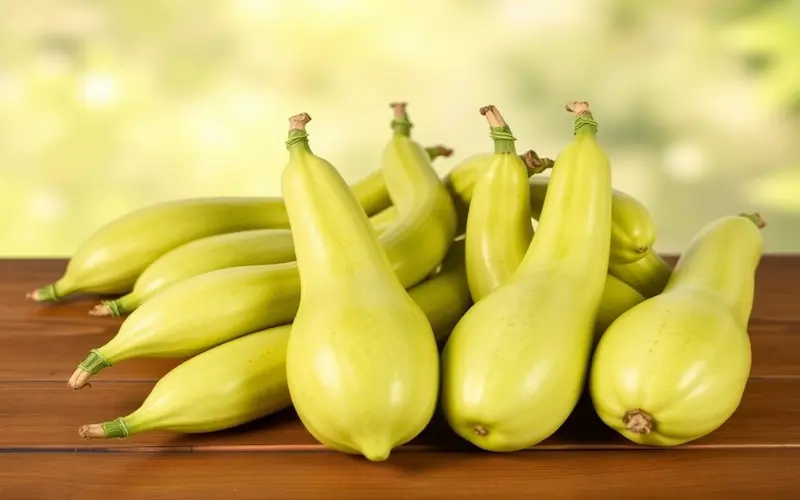

Squash
- Choose the Right Variety: Summer squash like zucchini is ideal for hot climates.
- Start from Seeds: Directly sow seeds in the garden after the last frost.
- Prepare the Soil: Use fertile, well-drained soil enriched with organic matter.
- Planting: Plant seeds 1 inch deep and space them 18-24 inches apart in rows.
- Sunlight: Ensure 6-8 hours of direct sunlight daily.
- Watering: Keep the soil consistently moist, especially during flowering and fruiting.
- Fertilization: Use a balanced fertilizer every 2-3 weeks to promote healthy growth.
- Pest Control: Look out for pests like squash bugs and cucumber beetles, and use organic methods to control them.
- Harvesting: Pick squash when small and tender, usually when they reach 6-8 inches in length.

Corn
- Choose the Right Variety: Sweet corn varieties like Golden Bantam suit hot climates.
- Start from Seeds: Directly sow seeds in the garden after the last frost.
- Prepare the Soil: Use rich, well-drained soil with plenty of organic matter.
- Planting: Plant seeds 1-2 inches deep and space them 12-18 inches apart in blocks rather than rows for better pollination.
- Sunlight: Ensure total sun exposure for at least 6-8 hours daily.
- Watering: Keep the soil consistently moist, especially during the tasseling and silking stages.
- Fertilization: Fertilize with a balanced fertilizer at planting time and again when the plants are about 12 inches tall.
- Pest Control: Monitor for pests like corn borers and aphids, and use organic pest control if needed.
- Harvesting: Harvest corn when the kernels are plump and milky, usually about 18-24 days after the silks appear.

Spinach
- Choose the Right Variety: Varieties like Bloomsdale Long Standing or Peshawari are heat-tolerant and suitable for summer growing.
- Start from Seeds: Sow seeds directly in the garden or containers.
- Prepare the Soil: Use well-drained, fertile soil enriched with compost.
- Planting: Sow seeds ½ inch deep, spacing them 4-6 inches apart.
- Sunlight: Spinach prefers partial shade, especially in hot climates.
- Watering: Keep the soil consistently moist to prevent the spinach from bolting (going to seed).
- Support the Plants: No additional support is needed for spinach.
- Fertilization: Use a nitrogen-rich fertilizer or compost every few weeks to encourage leafy growth. Pest and Disease Control: Watch for leaf miners and aphids; treat with organic solutions if necessary

FAQs About Summer Vegetables Season in Pakistan
The ideal time to plant summer vegetables in Pakistan is from February to May. Early planting ensures strong growth before the peak summer heat.
Most summer vegetables need deep watering 2-3 times a week, depending on the temperature. Daily watering may be required in extreme heat, especially for container plants.
Fast-growing summer vegetables in Pakistan are cucumbers, okra (ladyfinger), spinach, and squash. These vegetables are harvested within a few weeks of planting.
To protect your plants from the scorching sun:
- Use mulch to retain moisture.
- Water deeply early in the morning or late evening.
Provide shade using netting or cloth during peak summer hours.
Cucumbers, tomatoes, okra, eggplants, pumpkins, bitter gourd, okra, squash, and chilies are among Pakistan’s most popular summer vegetables.
Popular summer fruits in Pakistan are mangoes, watermelons, melons, lychees, and papayas. These fruits thrive in hot climates and are widely available in local markets.
Conclusion:
So guys, in this article, we have covered summer vegetables in Pakistan in detail. If you are new to gardening, I recommend starting with tomatoes and cucumbers because they are easy to grow and give quick results. Gardening in the summer is rewarding, especially when you enjoy fresh, homegrown veggies. Give it a try, and let me know which vegetables you plan to grow this season in the comments.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks



- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks