8 Steps to Growing Beetroot: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
Published: 18 Mar 2025
Growing beetroot is a rewarding experience for home gardeners and farmers alike. This nutrient-rich root vegetable is easy to cultivate and thrives in various climates with minimal care. If you follow the proper steps, you will achieve a healthy and bountiful beetroot harvest.
. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the essential steps of beetroot cultivation, from soil preparation to harvesting. If you want to expand your vegetable garden, check out our guide on growing bottle gourd for more tips on successful vegetable farming.

General Information Related Beetroot Cultivation
Beetroot, scientifically known as Beta vulgaris, is a versatile and nutritious root vegetable that thrives in various climates. Understanding its characteristics and growth requirements is crucial for successful cultivation.
Planting, Care, and Harvesting:
Beetroot farming is a simple yet rewarding process. From planting seeds to nurturing growing plants and finally harvesting vibrant roots, each stage requires careful attention.

Varieties and Recommendations:
Diverse varieties of Beetroot exist, each with its unique characteristics. Recommendations for cultivation in India and alternative names in various languages provide valuable insights for growers.
Environmental Requirements:
Beetroot cultivation is influenced by climatic and soil conditions. Discover the optimal temperature, sunlight, and soil types for a thriving Beetroot harvest.
Soil Preparation:
Land preparation plays a pivotal role in Beetroot cultivation. Learn the essential steps to ready the soil for planting, ensuring a nutrient-rich environment for robust growth.

Propagation of Beetroot:
Understanding the various methods of propagating Beetroot, including seed selection and preparation, sets the foundation for a successful crop.

Planting, Spacing, and Sowing:
Learn the precise techniques for planting Beetroot seeds, ensuring proper spacing and sowing practices to maximize yield.

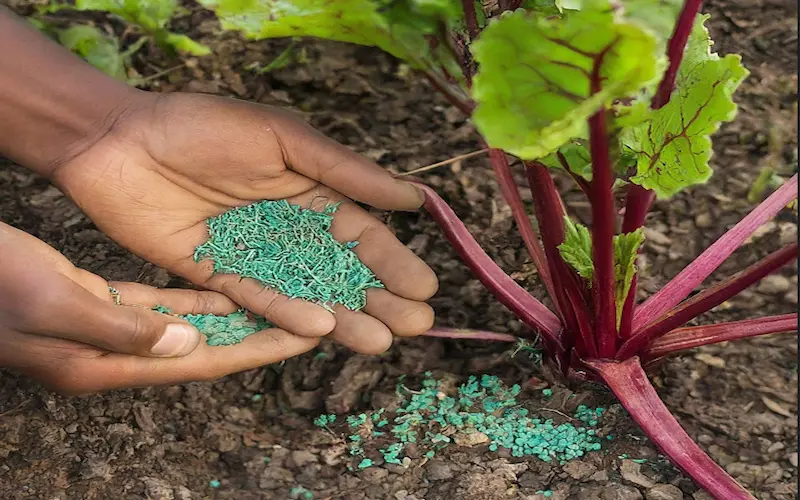
Fertilizer Requirement:
Uncover the specific fertilizer needs of Beetroot plants at different growth stages, promoting healthy development and a bountiful harvest.

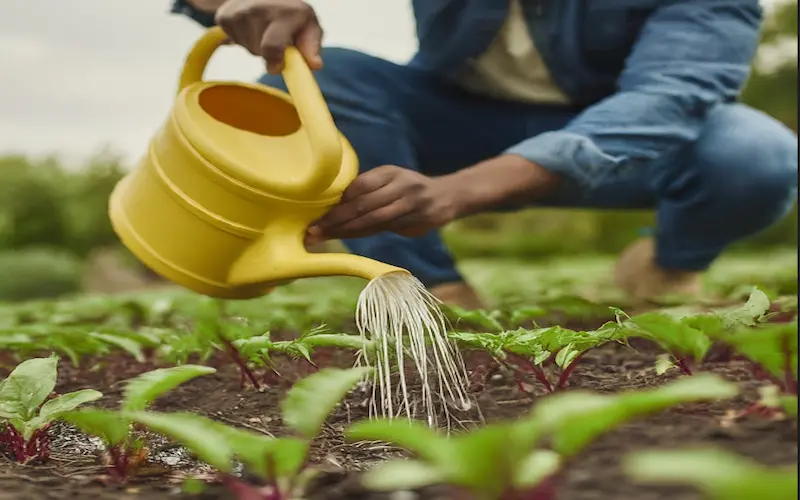
Water Requirement:
Adequate water is essential for Beetroot growth. Explore the ideal watering practices to maintain soil moisture and support the development of plump, juicy roots.

Intercultural Operations and Weed Control:
Navigate through intercultural operations and effective weed control strategies to maintain a weed-free and flourishing Beetroot crop.

Pests and Diseases:
Learn about common pests and diseases that affect beetroot plants and how to prevent them for a healthy, pest-free crop.
Explore everything about beetroot cultivation, from choosing the right variety to planting, caring, and overcoming challenges. This guide provides simple and practical steps for successful beetroot farming..
Varieties and Recommendations:
Beetroot cultivation offers a palette of varieties, each bringing its own flavor, color, and adaptability to the table. Understanding these varieties, along with recommendations for cultivation in India and alternative names in various languages, is fundamental to a successful harvest.
Recommended Varieties for Beetroot Cultivation.
Alternative Names in Different Languages:
Beetroot goes by various names worldwide, adding a linguistic richness to its cultivation. Whether it’s “Chukandar” in Hindi or “Remolacha” in Spanish, understanding these names aids in cross-cultural communication and sourcing the right seeds.
Characteristics of Popular Varieties:
Delve into the unique characteristics of popular Beetroot varieties. From size and shape to color and flavor profile, each variety brings a distinct quality to the table. For example, ‘Chioggia’ presents a striking pink-and-white ringed pattern, while ‘Boltardy’ is known for its reliability and consistent yield.
Adaptability to Different Climates:
Beetroot varieties exhibit varying degrees of adaptability to different climates. Some thrive in cooler temperatures, while others withstand heat better. By selecting the right variety based on your region’s climate, you set the stage for a successful harvest.
Hybrid Varieties and Improved Traits:
Explore hybrid varieties that have been developed through careful cross-breeding. These hybrids often boast improved traits such as disease resistance, enhanced color, or faster maturity, providing growers with advanced options for successful cultivation.
Considerations for Small-Scale and Home Gardens:
If you are growing beetroot in a small garden or home space then choosing compact varieties is key. Discover space-saving and container-friendly options that thrive in limited areas.
In India’s diverse agricultural climate, certain beetroot varieties perform exceptionally well. Options like Dhaval, Red Ace, and Detroit Dark Red adapt to different regions, helping farmers select the best fit for local conditions.
Knowing the right beetroot variety ensures a successful harvest. Whether you’re a commercial farmer in India or a home gardener exploring global options, this guide helps you make the best choice for your needs.
Environmental Requirements:
Successful beetroot cultivation depends on providing the right growing conditions. From climate requirements to soil preferences, understanding these factors is essential for a healthy and productive harvest.
Climatic Requirements:
Beetroot is a versatile vegetable that can adapt to various climates, but certain conditions optimize its growth. An ideal climate is generally defined by temperatures that typically range between 16 and 21 degrees Celsius (60 to 69 degrees Fahrenheit).However, Beetroot can also withstand warmer temperatures if provided with adequate moisture.
Sunlight Exposure:
Adequate sunlight is crucial for photosynthesis and the development of robust Beetroot plants. Ensure that the cultivation area receives at least 6-8 hours of sunlight daily to promote healthy foliage and root growth.
Soil Preferences:
Beetroot thrives in well-drained, loose, and fertile soil. A marginally acidic to normal soil pH somewhere in the range of 6.0 and 7.5 is ideal. Sandy loam or loamy soil textures are preferred, facilitating easy root penetration and preventing water logging.
Soil Enrichment and Organic Matter:
Preceding planting, improve the dirt with natural matter like all around spoiled fertilizer or matured compost. This enhances soil structure, fertility, and moisture retention, creating an ideal environment for Beetroot cultivation.
Moisture Requirements:
While Beetroot is relatively drought-tolerant, consistent moisture is essential, especially during the germination and root development stages. Adequate watering prevents the roots from becoming woody and ensures the production of tender, flavorful beets.
Protection from Extreme Conditions:
Beetroot plants are sensitive to extreme weather conditions. Provide protection during frost or excessive heat by implementing mulching or temporary shade structures. This safeguards the plants and promotes optimal growth.
Adaptation to Container Gardening:
For those with limited space, Beetroot can adapt well to container gardening. Select containers with proper drainage, use quality potting mix, and ensure adequate sunlight to enjoy a successful harvest even in confined spaces.
By aligning your Beetroot cultivation with these environmental requirements, you create an optimal setting for healthy growth and bountiful harvests. Whether you’re a backyard gardener or a commercial farmer, understanding and accommodating these factors contribute significantly to the success of your Beetroot crop.
Planting Process of Beetroot Cultivation
The journey from seed to harvest is a critical phase in Beetroot growing. Mastering the planting process ensures the development of healthy plants and flavorful roots. This section provides a step-by-step guide, covering everything from propagation to sowing and spacing.
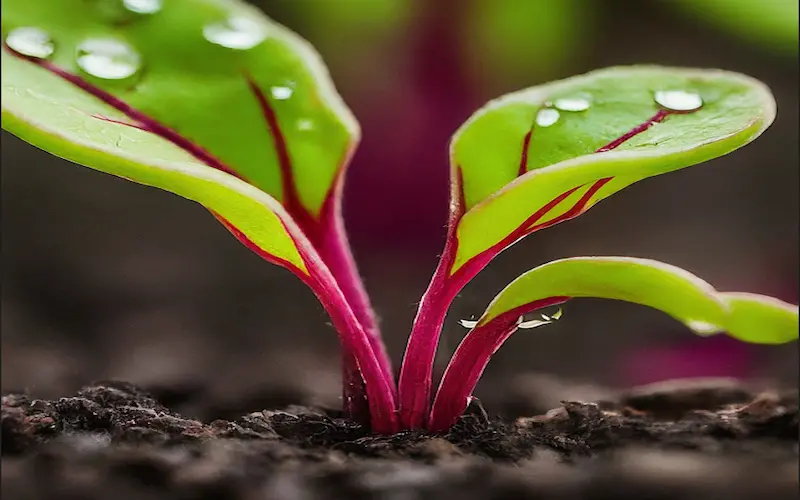

Propagation of Beetroot:
Beetroot is primarily propagated through seeds. Select high-quality seeds from reliable sources to ensure the success of your crop. Consider hybrid varieties for improved traits and disease resistance.
Land Preparation:
Prepare the planting site by clearing debris and weeds. Incorporate well-rotted compost or aged manure into the soil to enhance fertility and structure. Smooth the soil surface to create an even planting bed.
Seed Selection and Treatment:
Opt for Beetroot seeds that are uniform in size and free from damage. To enhance germination rates, consider soaking the seeds in water for a few hours before planting. This softens the seed coat and promotes quicker emergence.
Planting Techniques:
Plant Beetroot seeds directly in the prepared soil, placing them at a depth of about 1 inch. Space the seeds according to the recommended distance for the selected variety. Solidly press the dirt around the seeds to guarantee great seed-to-soil contact.
Sowing Guidelines:
Sow Beetroot seeds in rows, maintaining a row spacing of 12 to 18 inches. This facilitates proper air circulation and makes weeding and harvesting more manageable. Aim for a seed spacing of 2 to 4 inches within the rows.
Thinning Out Seedlings:
Once the seedlings emerge, thin them to achieve the recommended spacing. Proper thinning prevents overcrowding, allowing each plant sufficient space to develop a robust root system.
Watering Practices:
Adequate and consistent watering is crucial, especially during germination and root development. Use a gentle watering method to avoid displacing seeds and young seedlings. Maintain soil moisture throughout the growing season.
Container Gardening Considerations:
For those settling on compartment planting, select pots with waste openings and fill those with a quality preparing blend. Plant Beetroot seeds at the recommended depth, ensuring proper watering and sunlight for container-bound plants.
By following these planting guidelines, you set the stage for a successful Beetroot cultivation journey. From the careful selection of seeds to maintaining the right spacing and providing essential care, these steps contribute to robust plant growth and a satisfying harvest.
Nutrient Management:
To cultivate healthy and productive Beetroot plants, proper nutrient management is essential. This section explores the fertilizer requirements at different stages of Beetroot growth, ensuring a well-balanced and nourished crop.
Understanding Nutrient Needs:
Beetroot plants have specific nutrient requirements at different stages of their growth. Understanding these needs is crucial for providing the right nutrients in the right amounts.
Pre-Planting Soil Enrichment:
Before planting, enrich the soil with well-rotted compost or aged manure. This not only adds organic matter to the soil but also releases essential nutrients gradually, providing a nutrient-rich environment for young seedlings.
Fertilizer Types and Ratios:
Choose a balanced fertilizer with a ratio suitable for root crops. Manure with a fair N-P-K (Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium) extent, similar to 10-10-10 promotes overall plant health and encourages robust root development.
Application Timing:
Divide the fertilizer application into different stages. Apply a balanced fertilizer before planting to provide a nutrient boost for initial growth. Follow up with additional applications during the growing season, especially during the development of the root.
Topdressing Techniques:
Topdressing involves applying fertilizer on the soil surface around the plants. This technique minimizes root disturbance and ensures a steady release of nutrients. Apply topdressing when the plants are actively growing.
Organic Fertilizer Options:
For those inclined towards organic farming, consider using organic fertilizers such as well-rotted compost, manure, or organic formulations. These options provide nutrients in a slow-release manner, enhancing soil fertility naturally.
Adjusting Fertilizer Rates:
Monitor the growth of your Beetroot plants and adjust fertilizer rates accordingly. Excessive nitrogen can result in lush foliage but hinder root development, while phosphorus deficiency may lead to poor root growth.
Avoiding Excessive Fertilization:
Be cautious not to over-fertilize, as excessive nutrients can lead to imbalances, affecting plant health. Follow recommended guidelines and conduct soil tests periodically to assess nutrient levels.
By adopting a strategic approach to nutrient management, you provide Beetroot plants with the essential elements for robust growth, ensuring a nutrient-rich and flavorful harvest. Whether you choose synthetic or organic fertilizers, understanding the nutrient requirements of Beetroot plants contributes significantly to a successful cultivation experience.
Water Management:
Proper water management is a cornerstone of successful Beetroot growing. This section outlines the key considerations for ensuring adequate moisture throughout the growth stages, contributing to healthy plants and optimal root development.
Understanding Water Needs:
Beetroot plants require consistent moisture, especially during critical stages like germination, root development, and tuber enlargement. Understanding their water needs is crucial for achieving optimal growth.
Germination and Early Growth:
During germination, keep the soil consistently moist to facilitate seed emergence. Once seedlings appear, maintain even moisture to support their initial growth. Avoid waterlogged conditions, which can lead to seed and seedling rot.
Established Plant Care:
As Beetroot plants mature, continue to provide regular watering. Adequate moisture is essential for preventing the roots from becoming woody and ensuring the development of plump, tender beets. Aim for 1-1.5 inches of water per week.
Avoiding Water Stress:
Beetroot plants are sensitive to water stress, which can lead to stunted growth and poor-quality roots. Monitor soil moisture regularly and irrigate promptly during dry spells to prevent water stress.
Morning Watering Advantage:
Watering in the morning is advantageous, allowing the foliage to dry before evening. Wet foliage overnight increases the risk of fungal diseases. Morning watering ensures efficient water uptake without compromising plant health.
Container Gardening Considerations:
For container-grown Beetroot, closely monitor soil moisture as pots can dry out faster than garden beds. Adjust watering frequency based on the size of the container, prevailing weather conditions, and the plant’s growth stage.
Drainage Importance:
Ensure proper drainage to prevent water logging, which can lead to root rot. Well-draining soil allows excess water to escape, maintaining a healthy balance between moisture retention and drainage.
Rainfall Considerations:
While Beetroot can tolerate short dry periods, consistent rainfall or irrigation is crucial for optimal growth. Supplemental irrigation becomes essential during dry spells to ensure a continuous supply of moisture.
By mastering water management techniques, you provide Beetroot plants with the moisture they need for robust growth and high-quality root development. From germination to harvest, thoughtful irrigation practices contribute significantly to the success of your Beetroot cultivation endeavors.
Crop Management:
Effectively managing the Beetroot crop involves a combination of intercultural operations and weed control. This section guides growers through the essential tasks required to maintain a thriving and weed-free Beetroot plantation.
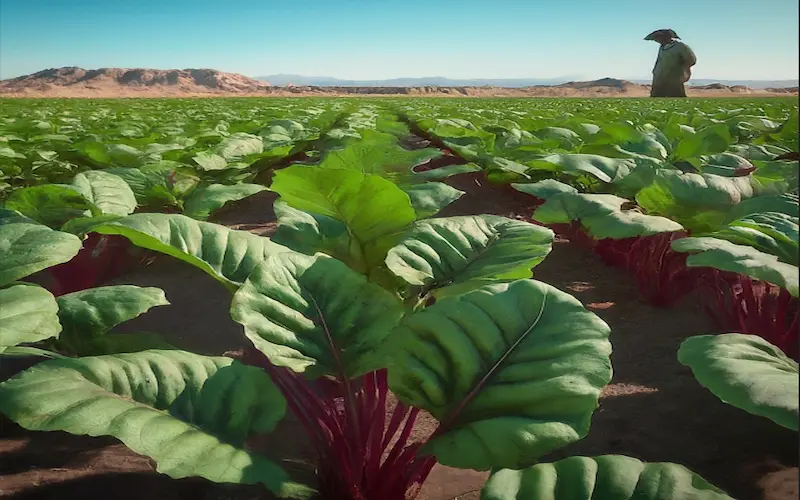

Intercultural Operations:
Intercultural operations refer to activities performed between the rows of Beetroot plants to ensure their proper growth and development. These include weeding, thinning, and other tasks that contribute to overall crop health.
Weed Control Strategies:
Weeds rival Beetroot plants for supplements, water, and daylight. Implement effective weed control strategies to minimize competition and create an environment where Beetroot can flourish.
Manual Weeding:
Regular manual weeding is essential to remove weeds that may hinder the growth of Beetroot plants. Be cautious while weeding to avoid damaging the shallow roots of young Beetroot plants.
Mulching Benefits for Weed Suppression:
Mulching not only retains soil moisture but also acts as a natural weed suppressant. Apply a layer of natural mulch around the plants to inhibit weed growth and reduce the need for frequent manual weeding.
Thinning Out Seedlings:
Thinning out excess seedlings is a critical intercultural operation. Overcrowding can lead to stunted growth and small-sized beets. Thin the seedlings to achieve the recommended spacing, allowing each plant sufficient room to thrive.
Maintaining Adequate Spacing:
Proper spacing between Beetroot plants is vital for good air circulation, preventing the onset of fungal diseases. Adequate spacing also facilitates efficient weeding and harvesting, contributing to overall crop management.
Fertilizer Application During Growth:
Throughout the growing season, monitor the nutrient needs of Beetroot plants. If deficiencies or imbalances are observed, address them promptly with appropriate fertilizer applications to sustain healthy growth.
Monitoring Plant Health:
Routinely examine Beetroot plants for indications of supplement inadequacies, nuisances, or infections. Early identification takes into consideration convenient mediation, forestalling expected difficulties and guaranteeing an effective reap.
Weed Identification and Removal:
Learn to identify common weeds that may infiltrate the Beetroot plantation. Swiftly remove these weeds to prevent them from establishing and competing with the crop.
Companion Planting for Pest Control:
Consider companion planting with pest-repelling plants like marigolds or basil. This natural pest control strategy can help minimize the risk of pests affecting your Beetroot crop.
Post-Harvest Cleanup:
After harvesting, conduct a thorough post-harvest cleanup to remove plant debris and minimize the risk of diseases or pests lingering in the area. This sets the stage for a healthy subsequent crop.
Effective crop management ensures that Beetroot plants receive the necessary care and attention throughout their growth cycle. By incorporating intercultural operations, weed control, and proactive monitoring, growers can create an environment conducive to robust Beetroot growth and a bountiful harvest.
Pest and Disease Management:
Protecting Beetroot crops from pests and diseases is essential to ensure a healthy and productive harvest. This section addresses common pests and diseases, offering identification tips and effective management strategies.
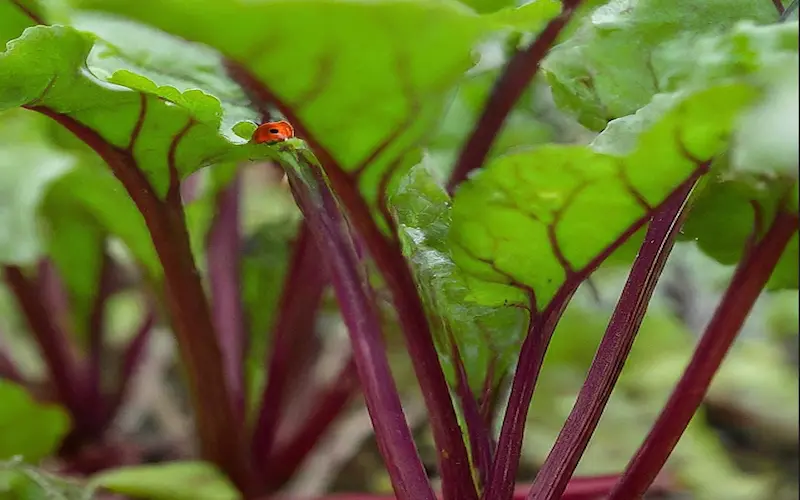

Common Pests of Beetroot:
Aphids: These small, sap-sucking insects can cluster on Beetroot leaves, causing yellowing and distortion. Utilize insecticidal cleanser or neem oil to control aphid populaces.
Flea Beetles: Identified by tiny jumping beetles, they create small holes in leaves. Introduce beneficial insects like ladybugs or use neem oil to deter flea beetles.
Cutworms: Larvae of these night-flying moths feed on young Beetroot plants, causing severe damage. Use physical barriers like collars around seedlings to protect them.
Diseases Affecting Beetroot:
1 Cercospora Leaf Spot: Identified by circular, dark spots on leaves, this fungal disease can lead to defoliation. Apply fungicides and practice crop rotation to manage leaf spot.
2 Rhizoctonia Root Rot: A soil-borne fungus causing damping-off and root rot. Plant disease-resistant varieties, practice proper soil drainage, and avoid overwatering to prevent its occurrence.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM):
Implement an Integrated Pest Management approach, combining biological, cultural, and chemical control methods. This holistic strategy minimizes the use of pesticides, promoting a more sustainable and environmentally friendly approach.
Beneficial Insects for Pest Control:
Encourage the presence of beneficial insects like ladybugs, parasitic wasps, and predatory beetles in your Beetroot garden. These natural predators help control pest populations without the need for chemical intervention.
Crop Rotation Practices:
Rotate Beetroot crops with unrelated plants to disrupt the life cycles of soil-borne pests and diseases. This practice reduces the risk of reinfestation and promotes overall soil health.
Early Detection and Treatment:
Regularly inspect Beetroot plants for signs of pests or diseases. Early detection allows for prompt treatment, minimizing the impact on crop health. Remove and destroy infected plant material to prevent the spread of diseases.
Organic Pest Control Options:
Explore organic pest control options such as neem oil, diatomaceous earth, or garlic spray. These natural remedies help manage pests without compromising the health of the Beetroot crop.
Fungal Disease Prevention:
To prevent fungal diseases, maintain proper spacing between Beetroot plants for good air circulation. Apply fungicides preventively, especially during periods of high humidity.
Resistant Varieties:
Choose Beetroot varieties that exhibit resistance to common pests and diseases prevalent in your region. Resistant varieties are often more resilient and require less intervention.
By incorporating these pest and disease management strategies into your Beetroot farming practices, you can minimize potential threats and safeguard the health of your crop. Vigilance, early intervention, and a holistic approach contribute to a successful and thriving Beetroot garden.
Beetroot Harvesting
Harvesting marks the culmination of your Beetroot cultivation journey. This section guides you through the optimal time to harvest, proper harvesting techniques, and tips for storing your freshly harvested beets.
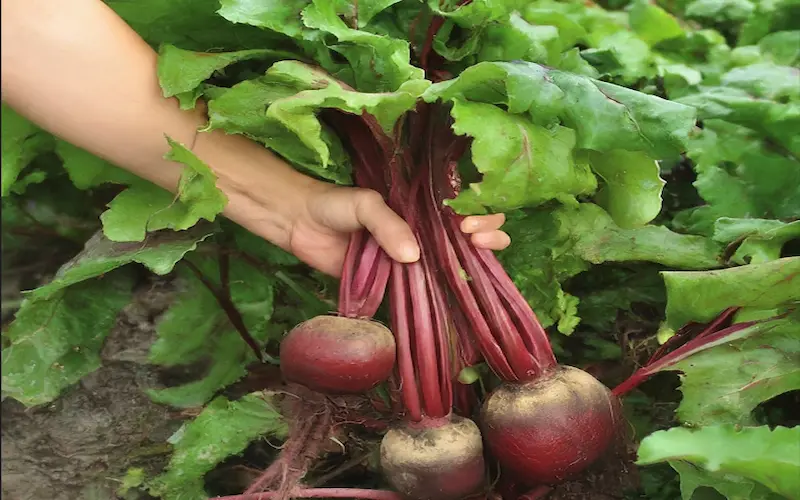

Determining Harvest Readiness:
Beetroot roots are typically ready for harvest 55 to 70 days after sowing. Size is a key indicator, with mature beets reaching 1.5 to 3 inches in diameter. Younger beets are more tender, while larger ones may have a coarser texture.
Harvesting Techniques:
Use a garden fork or hand shovel to carefully lift the beets from the soil. Insert the tool beside the beet, angling it slightly to avoid damaging the roots. Lift the beet gently to expose the entire root system.
Harvesting Successive Crops:
If you’ve planted beets in succession, harvest them as they reach the desired size. This staggered approach ensures a continuous supply of fresh beets throughout the growing season.
Tops Removal:
Trim the beet tops, leaving about an inch of stems attached to the beetroot. Leaving too much top can lead to moisture loss, while leaving too little can result in bleeding, where the color leaches from the beet.
Storage Preparation:
Before storing, gently brush off excess soil from the beets. Avoid washing them, as moisture can lead to rot during storage. Inspect the beets for any signs of damage or disease.
Beetroot Storage:
Refrigeration:
Store unwashed beets in the refrigerator. Place them in perforated plastic bags in the vegetable crisper. This method can keep beets fresh for several weeks.
Root Cellar:
For longer storage, consider a root cellar. Store beets in containers filled with sand or sawdust, ensuring good air circulation and humidity control.
Canning:
Preserve beets by canning them. This method involves cooking beets, peeling them, and packing them into sterilized jars with brine or vinegar.
Freezing Beetroot:
While beets can be frozen, they should be cooked and peeled first. Blanch the beets in boiling water, cool rapidly, peel, and cut into slices or cubes before freezing. Properly packaged, frozen beets can last for several months.
Utilizing Beet Greens:
Don’t discard beet greens; they are edible and nutritious. Separate the greens from the beets, wash them thoroughly, and use them in salads, sautés, or smoothies.
Monitoring Stored Beets:
Periodically check stored beets for any signs of spoilage. Remove any beets that show soft spots, mold, or rot to prevent the spread of issues to the rest of the stored crop.
By following these harvesting and storage guidelines, you ensure the freshness and quality of your Beetroot harvest. Whether you’re enjoying them immediately or preserving them for later use, these techniques contribute to a rewarding and sustainable Beetroot farming experience.
Step-by-Step Growing Guide:
Embarking on the journey of Beetroot farming requires a systematic approach, considering each stage from choosing seeds to harvesting. This step-by-step guide provides month-by-month insights and practical tips to ensure success throughout the growing season.
Selecting Seeds:
Planning:
Determine the planting area, considering sunlight exposure, soil quality, and available space. Plan for proper spacing between rows and individual plants.
Month-by-Month Guide:
Month 11-12: Post-Harvest Cleanup and Planning for Next Season:
Record Keeping: Take note of successes and challenges. Keep a record for planning the next Beetroot cultivation cycle.
This month-by-month guide serves as a roadmap for successful Beetroot farming. Whether you’re a fledgling or an accomplished landscaper, following these steps ensures a well-planned and rewarding journey from seed to harvest.
Faqs about Beetroot Farming
- Choose the Right Variety – Select a suitable beetroot variety based on your climate.
- Prepare the Soil – Ensure loose, well-drained soil with a pH of 6.0–7.5. Add compost for better fertility.
- Sow the Seeds – Plant seeds ½ inch deep and 2–3 inches apart in rows. Space rows 12 inches apart.
- Water Regularly – Keep the soil consistently moist but avoid overwatering.
- Thin the Seedlings – Once seedlings appear, thin them to 3–4 inches apart for proper growth.
- Fertilize as Needed – Use a balanced fertilizer or organic compost to boost growth.
- Monitor for Pests & Diseases – Watch for common pests like aphids and treat them early.
Harvest When Ready – Beetroots are ready in 50–70 days when they reach 1.5–3 inches in diameter
Beetroot typically takes 50–70 days to mature, depending on the variety and growing conditions. Baby beets can be harvested earlier, around 40 days after planting.
Beets grow best in cool weather, so the ideal months for planting are:
- Spring planting – February to April (for a summer harvest).
Fall planting – September to November (for a winter harvest)
Beetroot thrives in full sun but can tolerate partial shade. For the best growth, provide at least 6 hours of direct sunlight daily.
The best month to plant beetroot is May because they plant in warm climate weather which start from April.
Beetroot takes 7 to 9 weeks to grow from seed to harvest.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, growing beetroot is a rewarding experience when you follow the right steps. From selecting the best variety to providing proper care, each stage plays a crucial role in ensuring a healthy harvest. Whether you are a home gardener or a commercial farmer, understanding beetroot cultivation helps you achieve the best results.
If you’re interested in expanding your vegetable garden, explore our guide on summer vegetables in India to discover more crops that thrive in warm climates.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks



- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks