Unlocking the Secrets of Lettuce Growth Stages for a Bountiful Harvest”
Published: 5 Sep 2024
Lettuce is a versatile and popular leafy green vegetable that can be grown in various climates and enjoyed in multiple dishes. If you’re a beginner or an experienced gardener, understanding the different lettuce growth stages is essential for successful cultivation and optimal harvest.
In this comprehensive guide, I will explore the seven stages of growing lettuce, from seed to maturity, providing valuable insights and tips.
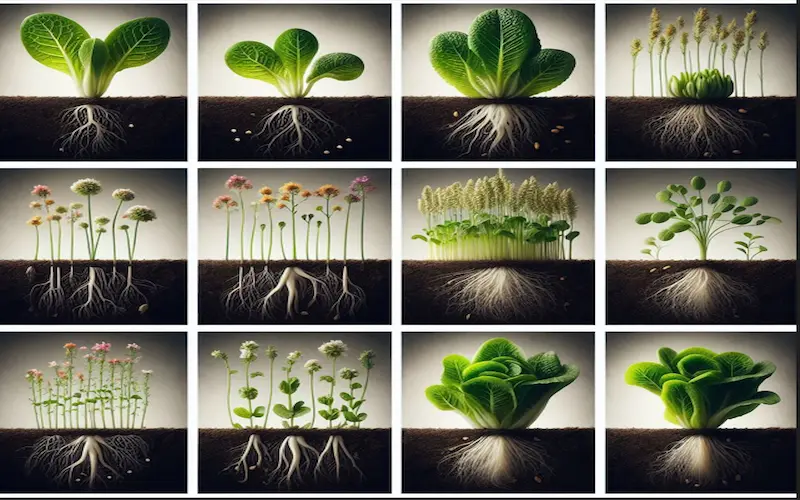

What Are the 8 Lettuce Growth Stages
Lettuce, a beloved leafy green, undergoes several growth stages from seed to harvest, each crucial for its development. It starts with germination, where the tiny seed awakens and roots into the soil. Next comes the seedling stage, marked by the emergence of delicate green shoots above the ground. At this point, tender leaves begin to unfurl, and the plant starts to establish its root system.
As days pass, the lettuce enters its vegetative phase, characterized by rapid leaf growth and the formation of a compact rosette. With ample sunlight and proper care, the plant flourishes, reaching maturity. Finally, it’s time for harvest, typically when the leaves are full-sized and vibrant, signalling the peak of flavor and nutritional value.
Understanding these growth stages empowers gardeners and farmers to nurture lettuce from its humble beginnings to a bountiful yield, ready to grace salads and sandwiches alike.
1. Planting Lettuce Seeds
Lettuce cultivation begins with the lettuce seeds. Lettuce seeds are tiny, typically about an eighth of an inch long, and come in white, black, tan, brown, or grey. Handling and storing lettuce seeds properly is essential to ensure their viability.
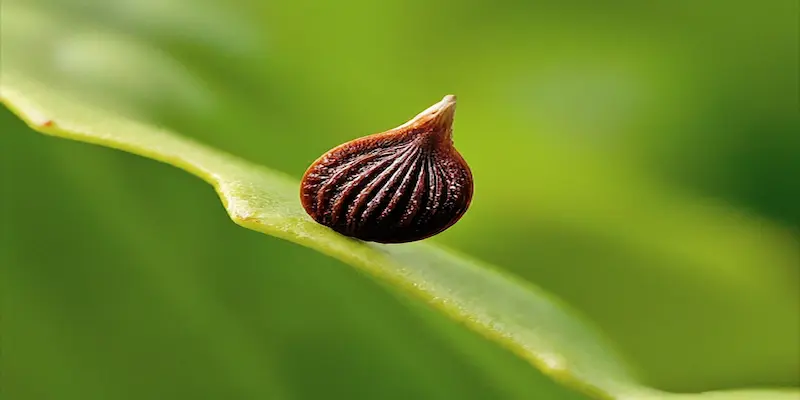

To make planting individual seeds easier, you can opt for pelleted lettuce seeds. These seeds are coated in a dissolvable coating, making handling and separating them more convenient. Whether you’re using regular or pelleted seeds, storing them in a cool, dry place to maintain their viability is crucial.
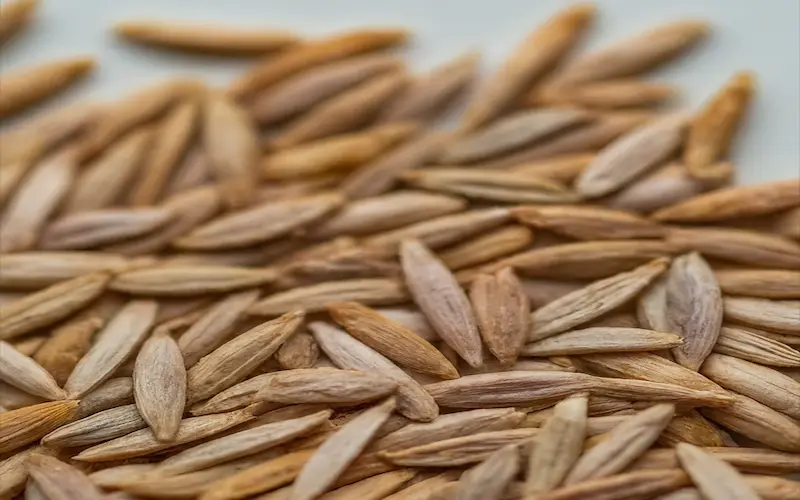

2. Germination: Emergence of Cotyledons
After planting lettuce seeds, the process of seed germination begins. Germination is when the seedling “wakes up” and starts to grow. Lettuce seeds require specific environmental conditions for successful germination, including moisture and proper temperature.
The optimal germination temperature for lettuce seeds is around 75°F. While they can germinate at temperatures as low as 40°F, temperatures above 80°F can result in spotty germination. To provide the ideal temperature for germination, you can start lettuce seeds indoors or choose a more remarkable period for outdoor planting.
Lettuce seeds absorb water during germination, causing the seed coat to soften. The seed then undergoes processes like respiration and metabolization, preparing for growth. The first root, the radicle, emerges, followed by the first above-ground tissue, the epicotyl. At this point, cotyledons, which are the first set of leaves, appear.
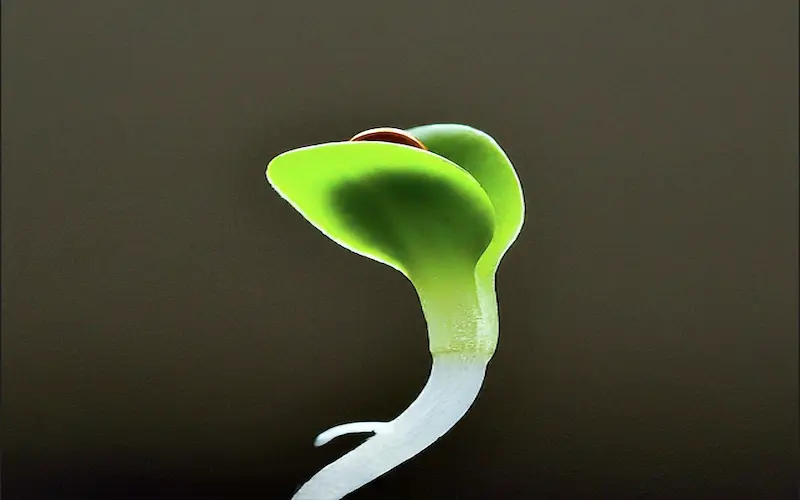

3. Seedling Stage
As the lettuce seedlings grow, they produce their first true leaves. These true leaves are distinct from the cotyledons and continue to grow as the plant matures. The seedlings require proper light, temperature, and moisture to thrive during this stage.
Maintaining adequate soil moisture is crucial during the seedling stage. Letting the soil dry out can result in plant death, while overwatering can lead to disease. It’s also an ideal time to thin lettuce seedlings if they are too close together. Thinning helps provide sufficient space for healthy growth and avoids overcrowding.
The seedling stage is an opportunity to harvest baby lettuce leaves if you prefer a more miniature, tender salad mix. The leaves are bite-sized and perfect for adding freshness to your meals.
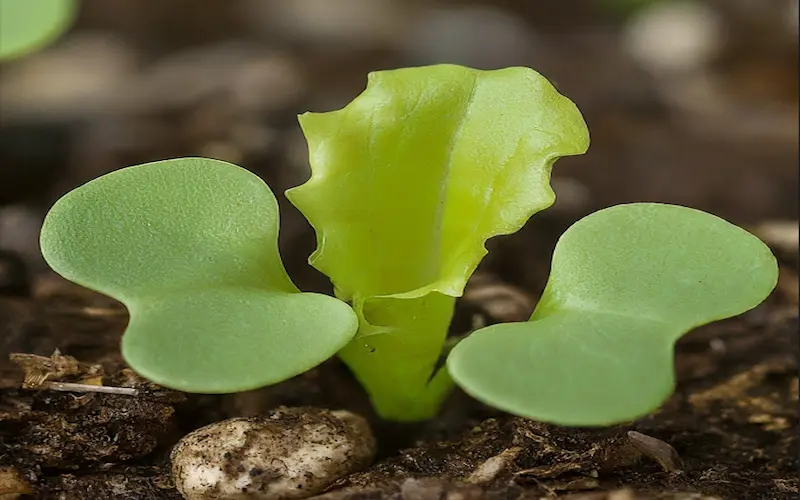

4. Rosette Stage of Lettuce Growth Stages
As lettuce plants continue to grow and produce new leaves, they enter the rosette stage. During this stage, the leaves take on a distinct circular shape. The appearance of the rosette stage can vary depending on the variety of lettuce.
For example, romaine lettuce has long, upright leaves, while butter lettuce displays lower and more ruffled leaves. The rosette stage typically lasts 25 to 50 days, depending on the variety of lettuce and the growing conditions. Growing lettuce successfully requires well-draining, nutrient-rich soil and consistent moisture, especially in cooler seasons. For a sustainable gardening approach, consider companion planting lettuce near a Lisbon lemon tree, which thrives in similar slightly acidic soil (pH 6.0–7.0).
While the plants are in the rosette stage, monitoring them for pests and diseases is essential. Pests like aphids, slugs, or armyworms can damage the leaves and hinder growth. Taking prompt action to address any pest issues will help ensure the health and productivity of your lettuce plants.
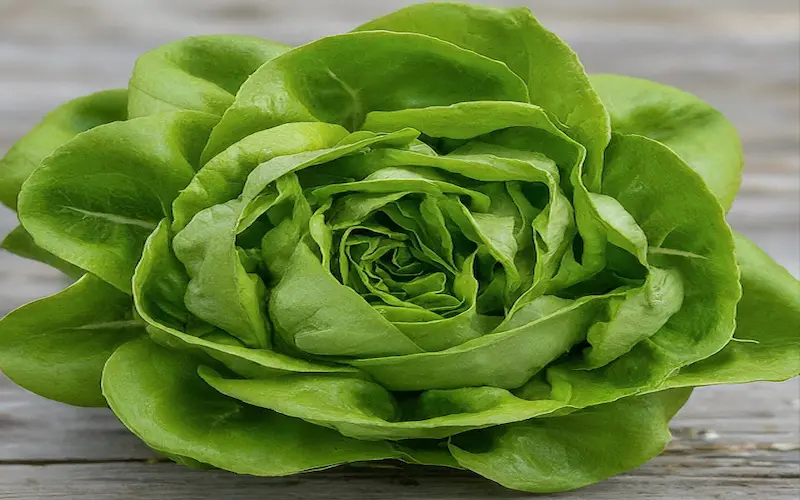

5. Cupping Stage
The cupping stage is short before the lettuce plant forms a dense head. During this stage, the lettuce leaves start to curl inward. The transient phase prepares the plant for the next growth stage.
The cupping stage typically lasts about a week; monitoring the plants closely during this time is essential. Ensuring proper moisture levels and providing adequate shade in hot climates can help the lettuce plants thrive and transition smoothly to the heading stage.
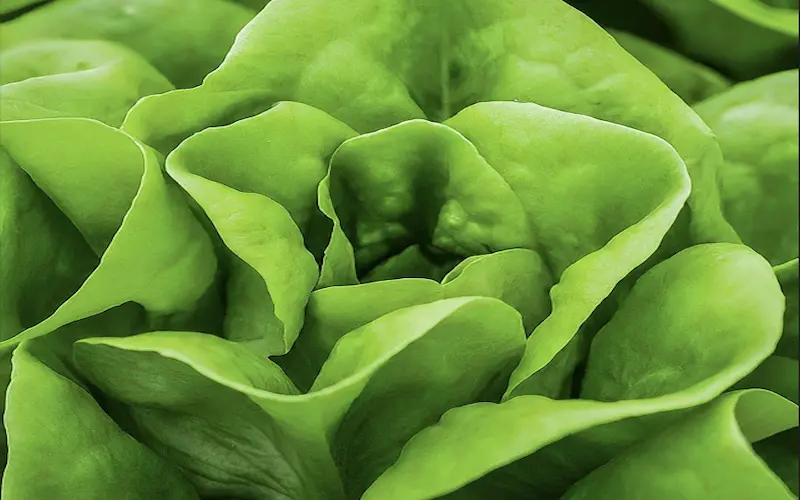

6. Heading stage
The heading stage is an exciting phase for lettuce growers. Aiming to harvest dense heads of lettuce, such as romaine or bibb lettuce. During this stage, the outermost leaves of the lettuce plant begin to curl inwards, covering the small centre leaves.
The duration of the heading stage can vary depending on the lettuce variety and the time of year. It typically ranges from 20 to 45 days. Monitoring the plants regularly during this stage is crucial to ensure they are harvested optimally.
To determine if a lettuce plant is ready for harvest, gently squeeze the leaves. If they hold up and don’t easily collapse, it’s a sign that the plant has formed a dense head and is ready to be harvested. Harvesting lettuce at the right time ensures the best texture and flavour.
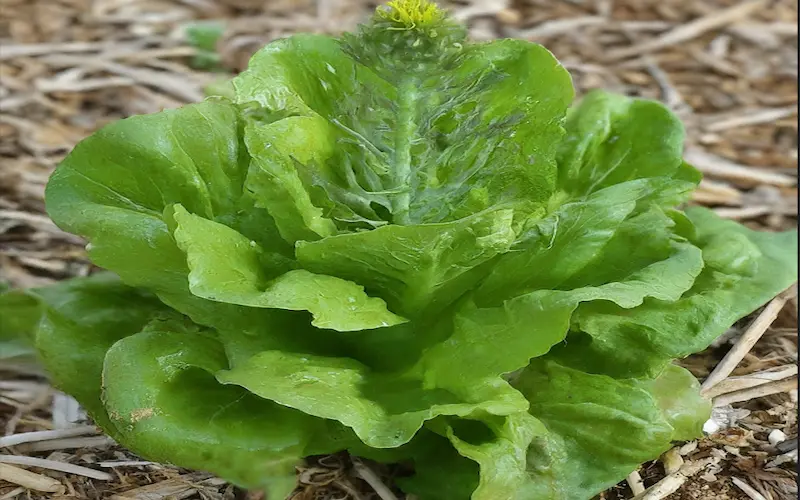

7. Bolting Stage
The bolting stage is a natural and significant part of the lettuce life cycle. The transition from vegetative to reproductive growth is referred to as bolting. It usually happens when the plant is subjected to extreme heat or other environmental stressors.
During the bolting stage, the lettuce plant undergoes noticeable changes. A rigid stalk emerges from the centre of the plant, transforming the once compact lettuce into a taller structure. Eventually, flowers appear on the top of the plant’s stalk. Successful pollination of these flowers leads to the development of lettuce seeds.
You’ll want to avoid the bolting stage if you’re growing lettuce for consumption. Bolting causes the leaves to become bitter and harsh. However, if you’re interested in saving lettuce seeds for future planting, this is the time to do so. Wait for a dry period, remove the seed heads, and collect the seeds for storage.
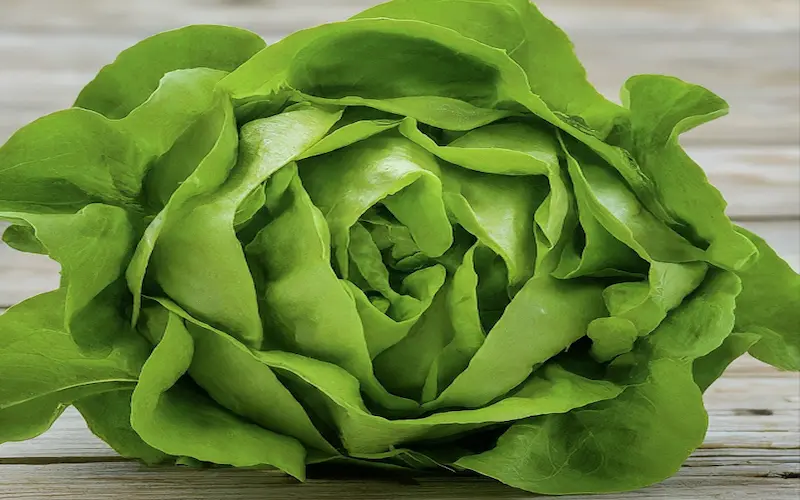

8. Harvesting
Harvesting lettuce at the right time ensures the best flavour and texture. The harvest timing depends on the variety of lettuce and your personal preferences.
For loose-leaf lettuce varieties, you can start harvesting individual leaves when they reach a desirable size. This allows the remaining leaves to grow, providing a continuous supply of fresh lettuce.
Head lettuce varieties, such as romaine or iceberg, are typically harvested when the heads are fully formed and dense. To gather these varieties, cut the entire head just above the base of the plant. Alternatively, you can remove the outer leaves as needed, allowing the inner leaves to continue developing.
It’s essential to harvest lettuce in the early morning when the leaves are crisp and at their freshest. Use a sharp knife or scissors to make clean cuts and minimize damage to the plant.

Lettuce Growth Chart
This 12-week chart of lettuce growth stages includes plant height measurements, leaf spread, and key weekly observations. Growth may vary depending on climate, soil quality, and lettuce variety. Regular monitoring and care are essential for successful lettuce cultivation.
| Week | Plant Height (inches) | Leaf Spread (inches) | Observations |
| 1 | 0.5 | 2 | Seedlings emerge |
| 2 | 1 | 3 | True leaves develop |
| 3 | 2 | 4 | Growth accelerates |
| 4 | 3 | 5 | Thinning may be required |
| 5 | 4 | 6 | Plants fill out |
| 6 | 5 | 7 | Regular watering and fertilizing |
| 7 | 6 | 8 | Begin harvesting outer leaves |
| 8 | 7 | 9 | Continued growth |
| 9 | 8 | 10 | Peak harvesting |
| 10 | 9 | 11 | Maintain moisture levels |
| 11 | 9.5 | 11.5 | Plants may bolt in warm weather |
| 12 | 10 | 12 | End of harvest, plants may start to bolt |
Romaine Lettuce Growing Stages
Romaine lettuce, or Cos lettuce, is a widespread variety known for its nutritional value and crisp, sweet-tasting leaves. It is highly favoured in salads, particularly in the classic Caesar salad. Culturing romaine lettuce involves several stages that require careful attention to ensure a healthy and robust crop.

The first stage in the growth of romaine lettuce is the germination process. This stage begins with planting the seeds in nutrient-rich soil. The seeds are typically planted about 1/4 to 1/2 inch deep and approximately 1 inch apart. Ideal conditions for germination include a soil temperature of about 40 degrees Fahrenheit and plenty of moisture. The seeds usually sprout within 7 to 10 days.
The next stage involves the growth of the seedlings. The lettuce plants must be thinned as they grow to prevent overcrowding, allowing for proper growth and development. Thinning usually occurs when the plants have reached about 2 to 3 inches in height. They should be spaced approximately 10 to 12 inches apart at this stage.
The maturation stage is next, during which the romaine lettuce develops its distinctive tall, elongated shape and deep green colour. This stage requires adequate watering and sunlight. Protecting the plants from pests and diseases at this stage is also crucial.
The final stage of the romaine lettuce growing process is harvesting. This typically occurs when the plants have reached about 8 to 12 inches in height, usually 60 to 70 days after planting. The leaves should be firm and crisp, and the hearts (the inner leaves) should be well-formed.
In conclusion, each stage in the growth of romaine lettuce plays a crucial role in dictating the quality of the final product. By understanding these stages and providing the necessary care at each point, growers can ensure a healthy, abundant yield of this popular lettuce variety.

Iceberg lettuce growing stages
Iceberg lettuce, scientifically termed Lactuca sativa, is widely known for its pale green leaves and crispy texture. This type of lettuce is often used in salads, sandwiches, and wraps due to its mild flavour and refreshing crunch. In addition to providing an excellent dish crunch, iceberg lettuce is packed with essential nutrients like vitamins A, K, and potassium.

The life cycle of iceberg lettuce involves several critical stages that determine the quality and yield of the crop. This process starts with seed sowing, generally performed in a controlled environment or a nursery to ensure optimal germination conditions.
Upon reaching a suitable size, typically after three to four weeks, the seedlings are transplanted to their permanent growing location. It’s crucial during this stage to maintain appropriate spacing between the plants to prevent overcrowding and stimulate healthy growth.
The next stage of growing iceberg lettuce is the vegetative phase, characterized by the formation and development of leaves. Lettuce plants require ample light, water, and nutrients to support their rapid growth during this period. It’s also essential to regularly monitor the crops for signs of pests or disease, as these can significantly impact yield and quality.
Following the vegetative stage is the critical stage of heading, where the iceberg lettuce forms its distinctive compact head. This stage usually takes about 50-60 days after transplanting. Proper care is needed because environmental stressors can cause the lettuce to bolt, leading to premature flowering and reduced quality.
The final stage in the growing process of iceberg lettuce is maturity and harvesting. When the heads become firm upon gentle squeezing and have reached an appropriate size, they are ready for harvest. Harvesting during the better parts of the day is pertinent to avoiding wilting and maintaining the lettuce’s crispness.
In conclusion, each stage of growing iceberg lettuce has unique requirements and challenges. Successful cultivation relies on careful planning, consistent care, and vigilant monitoring for potential issues. With these elements in place, growers can achieve a bountiful yield of high-quality iceberg lettuce.

Common Problems and Solutions
While lettuce is generally an easy crop to grow, it can be susceptible to specific issues. Here are a few common problems you may encounter and some solutions to address them:
- Bolting: Bolting can occur if the lettuce plants are exposed to high temperatures or experience stress. To prevent bolting, provide shade during hot periods, maintain consistent watering, and choose heat-tolerant varieties.
- Pests: Common lettuce pests include aphids, slugs, and snails. Monitor the plants regularly and take appropriate measures to control pests, such as using organic insecticides or physical barriers.
- Disease: Lettuce can be susceptible to powdery mildew, downy mildew, and root rot. Practice good sanitation, provide proper air circulation, and avoid overwatering to minimize disease risk.
- Nutrient deficiencies: Nutrient deficiencies can affect lettuce growth and lead to stunted or discoloured leaves. Conduct a soil test to identify nutrient deficiencies and amend the soil with organic fertilizers or compost.
Best Conditions to Grow Lettuce
Temperature: The Ideal range is 60°F to 70°F, as lettuce prefers cool weather.
Soil: Use loose, well-drained soil enriched with organic matter.
Sunlight: Provide at least 6 hours of direct sunlight daily; partial shade works during warmer months.
Watering: Watering lettuce is very important to keep the soil moist but avoid overwatering to prevent root rot.
Mulching: Apply mulch to retain moisture and reduce weed growth.
Planting Time: Sow seeds in early spring or fall for the best results during mild weather.
Faqs about Lettuce Growth Stages
Lettuce plants typically have a rosette of leaves, with either loose or compact heads, depending on the variety. The leaves are generally green, and their shape can vary, with some varieties having smooth, rounded leaves and others having more elongated leaves with distinct lobes or serrations. The plants have a low-growing habit, and their size can range from small to medium. Overall, lettuce plants have a fresh and vibrant appearance, with variations based on the type of lettuce being grown.
Lettuce seedlings typically have the following characteristics:
1. Cotyledons: The first leaves that emerge are cotyledons, which are often oval or heart-shaped and differ from the true leaves.
2. True Leaves: As the seedling grows, it develops true leaves that resemble the mature leaves of the specific lettuce variety. These leaves may have a more distinct shape, such as lobes or serrations.
3. Color: Initially, the seedlings are light green, and as they mature, they deepen in colour.
4. Size: Lettuce seedlings start small but increase. The size and appearance can vary depending on the specific lettuce type.
5. Stem: The stem of lettuce seedlings is usually thin and delicate, becoming more robust as the plant matures.
Overall, lettuce seedlings have a delicate and tender appearance, and their characteristics may vary based on the variety being grown.
Lettuce seeds typically germinate within five to ten days. Germination process depends upon the lettuce variety and environment. Lower temperatures can result in slower germination.
You can save lettuce seeds to grow hybrid varieties. Allow the lettuce plants to bolt and produce seed heads, then collect the dry seeds for storage.
Yes, lettuce can be grown in containers or pot. Choose compact varieties suitable for container or pot gardening and provide adequate drainage and moisture.
Yes, lettuce can be grown indoors with the right conditions. Provide sufficient light, moisture, and proper temperature for successful indoor lettuce cultivation.
Yes, chickens can eat lettuce. It’s a safe and healthy treat for them. Lettuce is low in calories and provides a good source of vitamins and fibre. However, it should be offered in moderation. It has a high water content and low nutritional value compared to other greens. Avoid giving them large quantities of lettuce, especially iceberg lettuce. If overfed, there is a chance of digestive issues.
Conclusion
Growing lettuce is a rewarding experience that allows you to enjoy fresh, crisp, nutritious greens straight from your garden. By understanding the eight stages of lettuce growth, from seed to maturity, you can optimize your cultivation practices and ensure a bountiful harvest. Remember to provide the right conditions, monitor for pests and diseases, and harvest at the appropriate time. With these tips and knowledge, you’ll be well on your way to growing your delicious lettuce.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks



- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks