The Ultimate Guide on Peas Growing Stages: Seed to Harvest
Published: 1 Jun 2024
Peas are a versatile and nutritious vegetable that can be grown in your backyard garden. Understanding the peas growing stages is essential for a successful harvest.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the peas’ growing season, the ideal growing time, and the required temperature and conditions. We will also provide you with a step-by-step peas-growing guide.
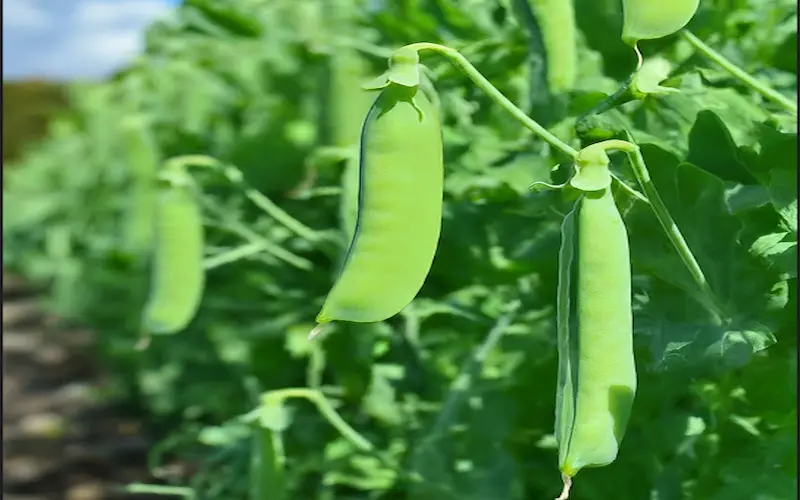

Peas Growing Season:
The pea’s growing season depends on your chosen variety and location. Generally, peas are cool-season crops that prefer temperatures between 55°F and 75°F (13°C to 24°C). They grow in regions with long, cool springs and short summers. It’s important to note that peas do not tolerate high heat or frost.
Peas Growing Time:
The time it takes for peas to grow from seed to harvest depends on the variety and growing conditions. On average, the time span ranges from 60 to 90 days. Early-maturing varieties may be ready for harvest in as little as 60 days, while maincrop varieties can take up to 90 days.
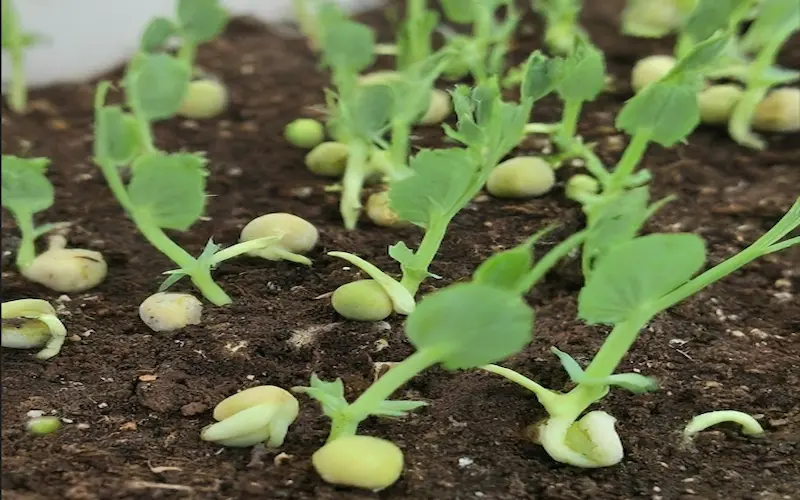

Peas Growing Temperature:
Peas prefer cooler temperatures and grow in mild climates. The ideal soil temperature for planting peas is around 45°F to 70°F (7°C to 21°C). If the temperature rises above 75°F (24°C), peas may become stressed and produce fewer pods. To extend the growing season, you can consider planting heat-tolerant varieties or providing shade during hot summers.
Peas Growing Conditions:
1. Soil
Peas thrive in well-draining soil with a pH level between 6.0 and 7.5. To improve fertility, prepare the soil by removing weeds, rocks, or debris and amend it with organic matter, such as compost or aged manure.
2. Sunlight
Peas require at least 6 hours of direct sunlight daily. Choose a location in your garden that receives ample sunlight. Use bush varieties that require less sunlight if you have limited sun exposure.
3. Watering
Peas need consistent moisture throughout their growing period. Water the plants deeply and regularly to keep the soil evenly moist. Avoid overwatering, as this can lead to root rot. Mulching can help retain soil moisture and prevent weed growth.
4. Support
Most pea varieties are climbers and require support. Install trellises, stakes, or netting to provide vertical support for the plants. This will prevent the vines from sprawling on the ground, improve air circulation, and make harvesting easier.
Peas Growing Stages:
Follow these step-by-step instructions for successful peas growing:
To ensure the best growth and yield, here are eight optimal peas growing stages:
1. Seed Selection:
Choose high-quality pea seeds from a reputable source. When selecting, consider the variety, growth habit (bush or climbing), and disease resistance.
2. Soil Preparation
Prepare the soil by removing weeds and loosening it with a garden fork or tiller. Incorporate organic matter, such as compost or aged manure, to improve soil fertility.
3. Sowing
Sow the pea seeds directly into the garden bed, about 1 to 1.5 inches deep and 2 inches apart. Space the rows 18 to 24 inches apart to allow for proper air circulation and ease of harvesting.
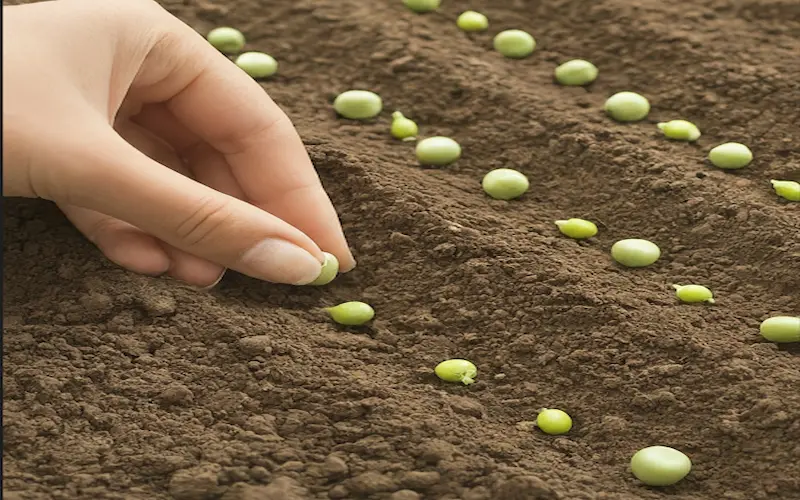

4. Watering
Water the seeds immediately after sowing and keep the soil consistently moist throughout the growing period. Avoid overhead watering, as it can encourage disease development. Instead, water is at the base of the plants.
5. Support
As the pea plants grow, provide support through trellises, stakes, or netting. Install them when the plants reach about 4 to 6 inches tall, and gently guide the vines to climb up.
6. Fertilization
Peas are light feeders but benefit from a balanced fertilizer application. When the plants are about 4 to 6 inches tall, apply a slow-release organic fertilizer according to the package instructions.
7. Pest and Disease Management
Monitor your pea plants regularly for pests like aphids, pea weevils, and powdery mildew. Use organic insecticides or insecticidal soap to control pests, and remove any infected plants to prevent the spread of diseases.
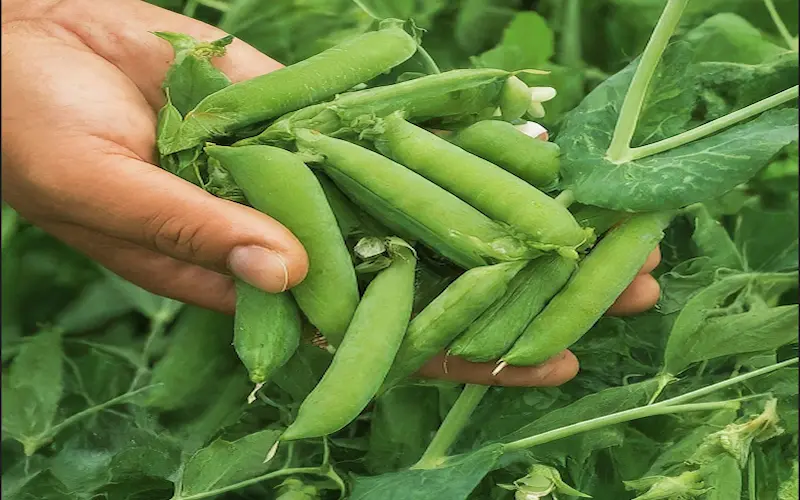
8. Harvesting
Harvest your peas when the pods are plump, fully developed, and tender. Pick them regularly to encourage continuous production. Use both hands to avoid damaging the delicate vines.

Related Questions and Answers
The stages of growing peas include seed germination, seedling emergence, vegetative growth, flowering, pod formation, and harvest.
Pea seeds typically germinate for 7 to 10 days, depending on the variety and growing conditions.
The vegetative growth stage of peas can last anywhere from 30 to 60 days, depending on the variety and environmental factors.
Peas usually flower around 45 to 60 days after planting, depending on the variety and growing conditions.
Pea pods typically form about 7 to 10 days after flowering.
Peas are best harvested when the pods are plump, firm, and bright green. This usually occurs about 60 to 70 days after planting but can vary depending on the variety
Conclusion:
Understanding the peas growing stages can ensure a successful and bountiful harvest. Remember to consider the peas’ growing season, ideal time, temperature requirements, and optimal growing conditions. Follow our step-by-step peas growing guide, and you’ll enjoy fresh, flavourful peas from your garden in no time.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks



- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks